Difference between revisions of "FOOD BASE"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<tr style='mso-yfti-irow:0;mso-yfti-firstrow:yes'> | <tr style='mso-yfti-irow:0;mso-yfti-firstrow:yes'> | ||
<td width=40% valign=bottom align=left style='width:2.05in;padding:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt'> | <td width=40% valign=bottom align=left style='width:2.05in;padding:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt'> | ||
| − | <p class=MsoNormal> | + | <p class=MsoNormal></p> |
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
===''Food Base''=== | ===''Food Base''=== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:USGS- Food web of the Grand Canyon- SLIDE.jpg |800px]] | |
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File:Invertebrate production exhibits stepped declines downstrea from tributaries Slide 23.jpg |600px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 86: | Line 87: | ||
*'''[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/15jan20/Attach_11.pdf/ Invertebrate drift in Glen Canyon 2007-2013]''' | *'''[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/15jan20/Attach_11.pdf/ Invertebrate drift in Glen Canyon 2007-2013]''' | ||
| + | 2014 | ||
| + | *'''[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14jan30/Attach_05a.pdf/ Foodbase Enhancement Suggestions from Federation of Fly Fishers]''' | ||
| + | *'''[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14jan30/Attach_05b.pdf/ Foodbase Findings]''' | ||
| + | *'''[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14jan30/AR_Kennedy_Foodweb_Update.pdf/ Foodbase Update]''' | ||
2013 | 2013 | ||
| Line 91: | Line 96: | ||
*'''[http://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2013/3039/fs2013-3039.pdf/ Native and nonnative fish populations of the Colorado River are food limited - Evidence from new food web analyses]''' | *'''[http://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2013/3039/fs2013-3039.pdf/ Native and nonnative fish populations of the Colorado River are food limited - Evidence from new food web analyses]''' | ||
*'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/WellardKelley_et%20al.%202013.pdf/ Macroinvertebrate diets reflect tributary inputs and turbidity-driven changes in food availability in the Colorado River downstream of Glen Canyon Dam]''' | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/WellardKelley_et%20al.%202013.pdf/ Macroinvertebrate diets reflect tributary inputs and turbidity-driven changes in food availability in the Colorado River downstream of Glen Canyon Dam]''' | ||
| − | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Kennedy%20et%20al.%20FWB%20proofs.pdf/ The relation between invertebrate drift and two primary controls, discharge and benthic densities, in a large | + | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Kennedy%20et%20al.%20FWB%20proofs.pdf/ The relation between invertebrate drift and two primary controls, discharge and benthic densities, in a large regulated river]''' |
| − | regulated river]''' | + | |
2012 | 2012 | ||
| Line 99: | Line 103: | ||
2011 | 2011 | ||
| − | *'''http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Cross%20et%20al.%202011_EA.pdf/ Ecosystem ecology meets adaptive management: food web response to a controlled flood on the Colorado River, Glen Canyon]''' | + | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Cross%20et%20al.%202011_EA.pdf/ Ecosystem ecology meets adaptive management: food web response to a controlled flood on the Colorado River, Glen Canyon]''' |
| − | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Donner_Thesis%202011.pdf/ SECONDARY PRODUCTION RATES, CONSUMPTION RATES, AND TROPHIC | + | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Donner_Thesis%202011.pdf/ SECONDARY PRODUCTION RATES, CONSUMPTION RATES, AND TROPHIC BASIS OF PRODUCTION OF FISHES IN THE COLORADO RIVER, GRAND CANYON, AZ: AN ASSESSMENT OF POTENTIAL COMPETITION FOR FOOD]''' |
*'''[http://http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Zahn_Thesis_2011.pdf/ DIET OVERLAP AND COMPETITION AMONG NATIVE AND NON-NATIVE SMALL-BODIED FISHES IN THE COLORADO RIVER, GRAND CANYON, ARIZONA]''' | *'''[http://http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Zahn_Thesis_2011.pdf/ DIET OVERLAP AND COMPETITION AMONG NATIVE AND NON-NATIVE SMALL-BODIED FISHES IN THE COLORADO RIVER, GRAND CANYON, ARIZONA]''' | ||
| Line 123: | Line 127: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ||
---- | ---- | ||
*'''[http://www.redorbit.com/news/science/1112927299/lessons-from-grand-canyon-dams-destabilize-river-food-webs-082013/ Red Orbit - Lessons From The Grand Canyon: Dams Destabilize River Food Webs]''' | *'''[http://www.redorbit.com/news/science/1112927299/lessons-from-grand-canyon-dams-destabilize-river-food-webs-082013/ Red Orbit - Lessons From The Grand Canyon: Dams Destabilize River Food Webs]''' | ||
Revision as of 16:29, 15 April 2016
|
|
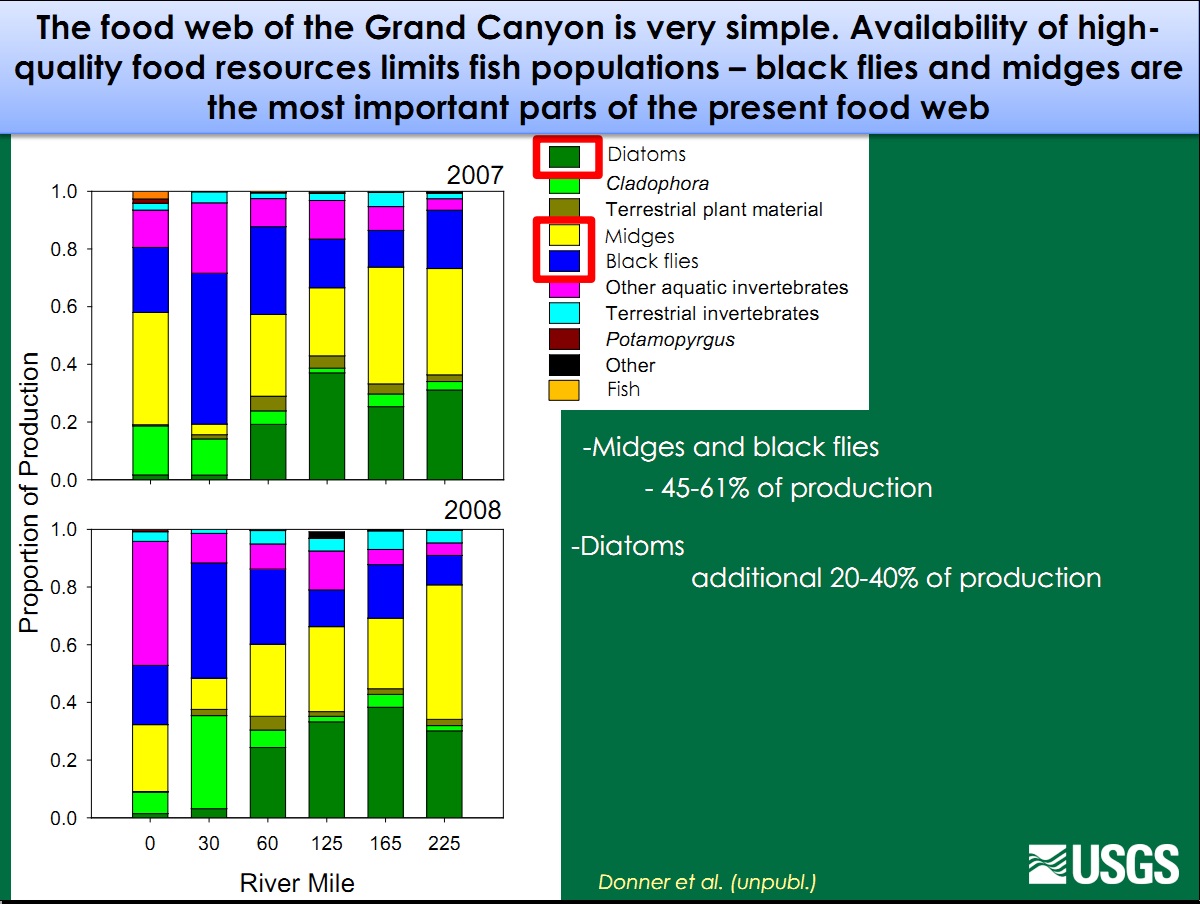
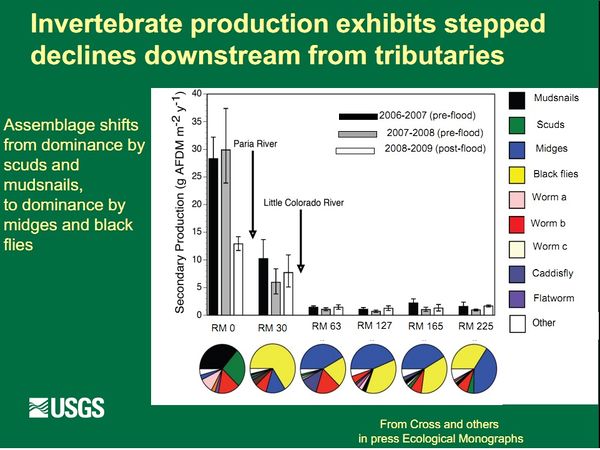
Food Base USGS- GCMRC DefinitionThe Colorado River below Glen Canyon Dam has been altered by dam-induced modifications to the river’s flow, temperature, and sediment supply. Nonnative species have also changed the natural system. Nonnative fish are thought to prey on and compete with native fish, including the endangered humpback chub (Gila cypha). These impacts have likely changed both the amount and sources of energy that fuel the aquatic food web and the flows of energy within the food web. Installation of the dam created a relatively clear, cool aquatic environment below the dam that now allows aquatic plants to capture the sun’s energy, and they in turn are now consumed by a few species, including scuds (Gammarus lacustris), midges (Family: Chironomidae), blackflies (Simulium arcticum), and New Zealand mudsnails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). The first three species can provide food for both native and nonnative fishes, but fish cannot digest the New Zealand mudsnail.
|
| TBD (Motions) |
TBD (TBD) |
TBD (TBD) |
|---|