Difference between revisions of "FOOD BASE"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">News</h2> | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">News</h2> | ||
| + | 2013 | ||
| + | *'''[http://www.redorbit.com/news/science/1112927299/lessons-from-grand-canyon-dams-destabilize-river-food-webs-082013/ Lessons From The Grand Canyon: Dams Destabilize River Food Webs]''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| Line 101: | Line 103: | ||
2012 | 2012 | ||
| − | |||
*'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Hall%20et%20al.%202012.pdf Air –water oxygen exchange in a large whitewater river]''' | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Hall%20et%20al.%202012.pdf Air –water oxygen exchange in a large whitewater river]''' | ||
| + | *'''[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/01apr12/Attach_08a.pdf Temperatures, TCD, and Food Base]''' | ||
2011 | 2011 | ||
| − | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Cross%20et%20al.%202011_EA.pdf Ecosystem ecology meets adaptive management: | + | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Cross%20et%20al.%202011_EA.pdf Ecosystem ecology meets adaptive management: Food web response to a controlled flood on the Colorado River, Glen Canyon]''' |
| − | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Donner_Thesis%202011.pdf | + | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Donner_Thesis%202011.pdf Secondary production rates, consumption rates, and trophic basis of production of fishes in the Colorado River, Grand Canyon, AZ: An assessment of potential competition for food]''' |
| − | *'''[http://http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Zahn_Thesis_2011.pdf | + | *'''[http://http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Zahn_Thesis_2011.pdf Diet overlap and competition among native and non-native small-bodied fishes in the Colorado River, Arizona]''' |
2010 | 2010 | ||
| − | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Wellard%20Kelly_Thesis%202010.pdf | + | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Wellard%20Kelly_Thesis%202010.pdf Resource composition and macroinvertebrate resource consumption in the Colorado River below Glen Canyon Dam]''' |
*'''[http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2010/1031/of2010-1031.pdf Short-Term Effects of the 2008 High-Flow Experiment on Macroinvertebrates in Colorado River Below Glen Canyon Dam, Arizona]''' | *'''[http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2010/1031/of2010-1031.pdf Short-Term Effects of the 2008 High-Flow Experiment on Macroinvertebrates in Colorado River Below Glen Canyon Dam, Arizona]''' | ||
*'''[http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2010/1075/of2010-1075.pdf Basal Resources in Backwaters of the Colorado River Below Glen Canyon Dam—Effects of Discharge Regimes and Comparison with Mainstem Depositional Environments]''' | *'''[http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2010/1075/of2010-1075.pdf Basal Resources in Backwaters of the Colorado River Below Glen Canyon Dam—Effects of Discharge Regimes and Comparison with Mainstem Depositional Environments]''' | ||
| Line 121: | Line 123: | ||
1981 | 1981 | ||
*'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/library/reports/GrandCanyon/Carothers1981.pdf A survey of the aquatic flora and fauna of the Grand Canyon]''' | *'''[http://www.gcmrc.gov/library/reports/GrandCanyon/Carothers1981.pdf A survey of the aquatic flora and fauna of the Grand Canyon]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1959 | ||
| + | *'''[http://core.tdar.org/document/92630/ecological-studies-of-the-flora-and-fauna-in-glen-canyon Ecological Studies of the Flora and Fauna in Glen Canyon (Woodbury 1959)]''' | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Other Stuff</h2> | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Other Stuff</h2> | ||
| Line 126: | Line 132: | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
*Black Flies and Midges fuel RBT growth. | *Black Flies and Midges fuel RBT growth. | ||
| − | *Black Flies and Midges respond positively to HFE's | + | *Black Flies and Midges respond positively to spring HFE's |
*Mud Snails were introduced to the system around 1995. | *Mud Snails were introduced to the system around 1995. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 135: | Line 141: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 12:40, 9 May 2016
|
|
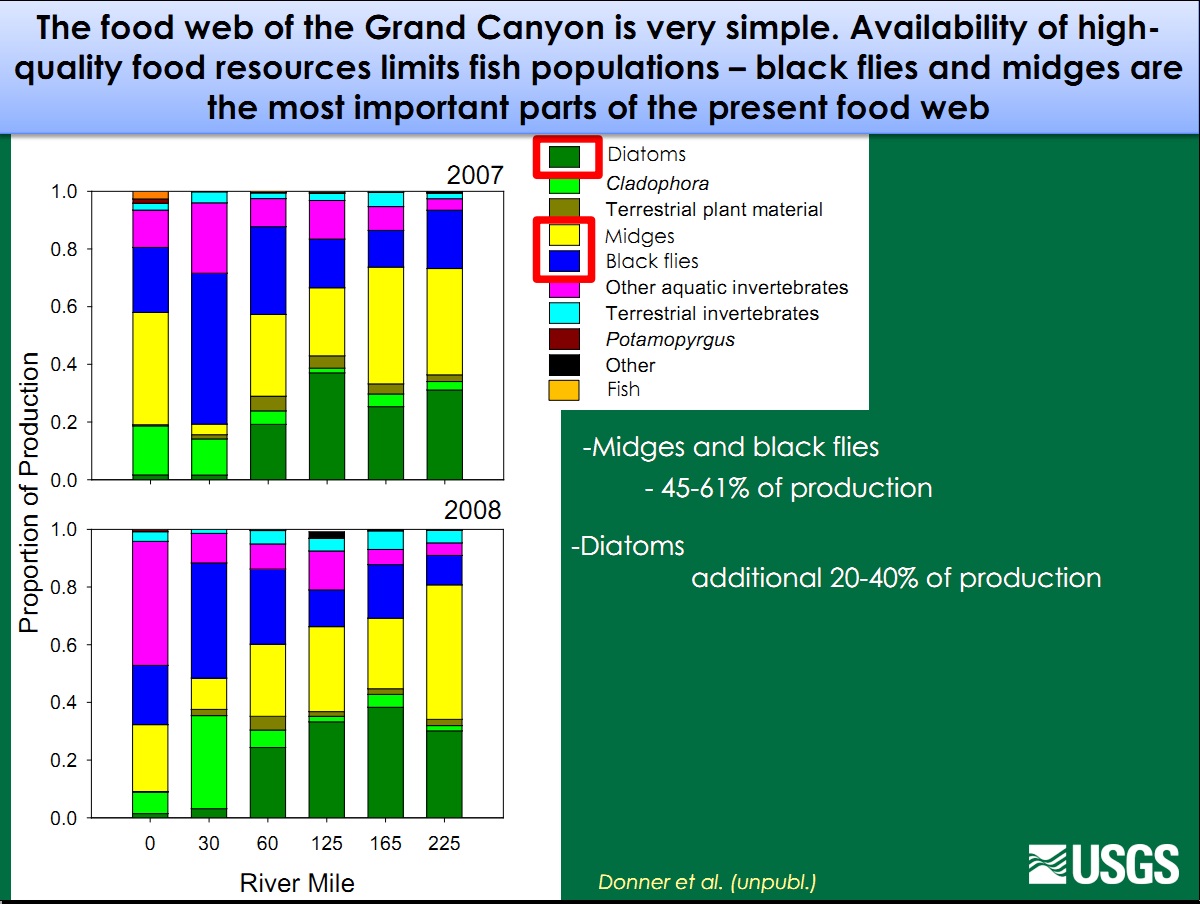
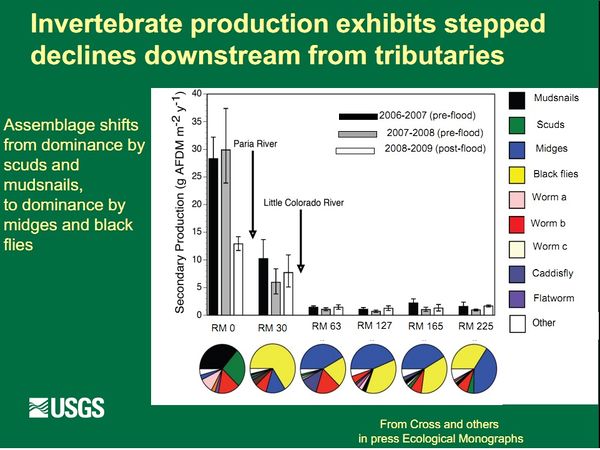
Food Base USGS- GCMRC DefinitionThe Colorado River below Glen Canyon Dam has been altered by dam-induced modifications to the river’s flow, temperature, and sediment supply. Nonnative species have also changed the natural system. Nonnative fish are thought to prey on and compete with native fish, including the endangered humpback chub (Gila cypha). These impacts have likely changed both the amount and sources of energy that fuel the aquatic food web and the flows of energy within the food web. Installation of the dam created a relatively clear, cool aquatic environment below the dam that now allows aquatic plants to capture the sun’s energy, and they in turn are now consumed by a few species, including scuds (Gammarus lacustris), midges (Family: Chironomidae), blackflies (Simulium arcticum), and New Zealand mudsnails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). The first three species can provide food for both native and nonnative fishes, but fish cannot digest the New Zealand mudsnail.
|
| TBD (Motions) |
TBD (TBD) |
TBD (TBD) |
|---|