|
|
LTEMP Experimental Action: Native and Nonnative Plant Management and Experimental Treatments (BA, pages 41-42) [4]
|
|
Experimental riparian vegetation treatment activities would be implemented by NPS
under the proposed action and would modify the cover and distribution of riparian plant
communities along the Colorado River. All activities would be consistent with NPS
Management Policies (NPS 2006) and would occur only within the Colorado River
Ecosystem in areas that are influenced by dam operations. NPS would work with tribal
partners and GCMRC to experimentally implement and evaluate a number of vegetation
control and native replanting activities on the riparian vegetation within the Colorado
River Ecosystem in GCNP and GCNRA. These activities would include ongoing
monitoring and removal of selected nonnative plant species, systematic removal of
nonnative vegetation at targeted sites, and native replanting at targeted sites, which may
include complete removal of tamarisk (both live and dead) and re-vegetation with native
plants. Treatments would include the control of nonnative plant species and revegetation
with native plant species.
|
Experimental Vegetation Treatment and Mitigation (LTEMP ROD pg 19)
|
|
As part of LTEMP, experimental riparian vegetation treatment was included as mitigation for
dam operations within CRE. Vegetation treatment actions on NPS managed lands will be
implemented by NPS consistent with NPS Management Policies (NPS 2006) and will occur only
within the CRE in areas that are influenced by dam operations. The NPS will work with tribal
partners and GCMRC to experimentally implement and evaluate a number of vegetation control
and native replanting activities on the riparian vegetation within the Colorado River Ecosystem
in GCNP and GCNRA. These activities would include ongoing monitoring and removal of
selected nonnative plants, species in the corridor, systematic removal of nonnative vegetation at
targeted sites, and native replanting at targeted sites and subreaches, which may include
complete removal of tamarisk (both live and dead) and revegetation with native vegetation.
Treatments would fall into two broad categories, including the control of nonnative plant species
and revegetation with native plant species. Principal elements of this experimental riparian
vegetation proposal include:
- Control nonnative plant species affected by dam operations, including tamarisk and other highly invasive species;
- Develop native plant materials for replanting through partnerships and the use of regional greenhouses;
- Replant native plant species to priority sites along the river corridor, including native species of interest to tribes;
- Remove vegetation encroaching on campsites; and
- Manage vegetation to assist with cultural site protection.
|
Papers and Presentations
|
|
2017
2016
- Palmquist, E.C., Ralston, B.R., Sarr, D., Merritt D.M., Shafroth, P.B., and Scott, J.A., 2017, Functional traits and ecological affinities of riparian plants along the Colorado River in Grand Canyon: Western North American Naturalist, v. 77, no. 1, p. 22--30
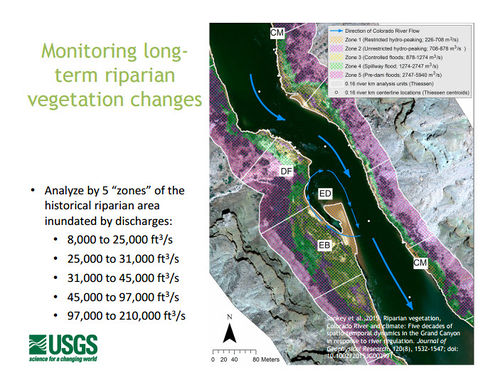
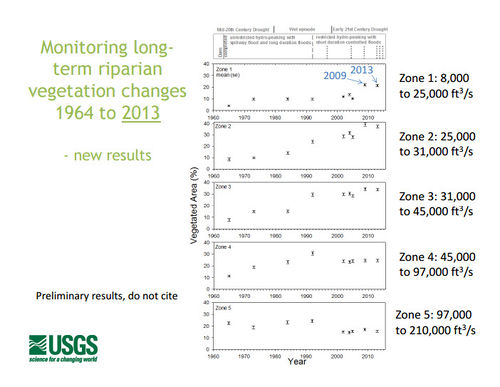
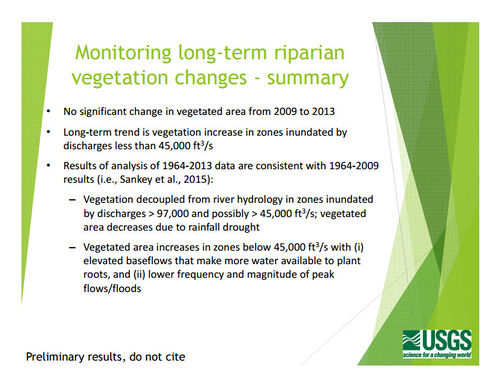
- Riparian Vegetation Monitoring with Remote Sensing
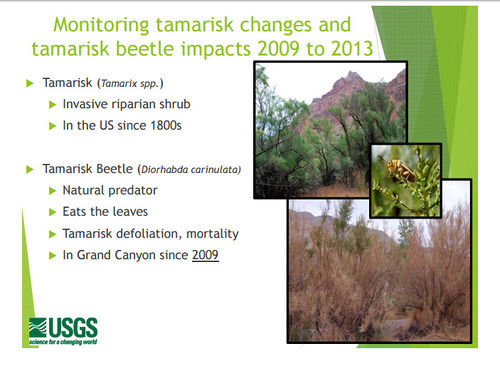
- Sankey et al. 2016, Remote Sensing of Tamarisk Biomass, Insect Herbivory, and Defoliation: Novel Methods in the Grand Canyon Region, Arizona: Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 82(8), pp. 645-652
- Linkages between controlled floods, eddy sandbar dynamics, and riparian vegetation along the Colorado River in Marble Canyon, Arizona, USA
- Riparian vegetation monitoring with remote sensing
- Southern Paiute Consortium Vegetation and Cultural Resource Monitoring Program
- Historical Changes to Culturally-Important Riparian Plants along the Colorado River: A Progress Report on Project 12
- Report of Riparian Vegetation Workshop, June 23-25, 2015 in Flagstaff, AZ
2015
2013
2012
|
Other Stuff
|
General Plant Species
- Approximately 129 vegetation communities, Over 850 species have been reported from GCNRA, and over 1,750 vascular plant species from GCNP (NPS CFMP-EA_pg 19)
- Riparian communities are dominated by species such as coyote and seep willows, arrowweed, western honey mesquite, catclaw acacia, and exotic tamarisk with many other species present.
- Desert Scrub communities are dominated by species such as creosote, white bursage, brittle bush, ocotillo, four-wing saltbush, big sagebrush, ephedra, dropseed, brome grasses, and many other species.
- Approximately 11% of flora in GCNP and GC reach is exotic.
|
|