Difference between revisions of "Water Quality Page"
From Glen Canyon Dam AMP
(template for water quality page) |
(add 201410 NDW Article Our Water Keeping it Clean) |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<tr style='mso-yfti-irow:0;mso-yfti-firstrow:yes'> | <tr style='mso-yfti-irow:0;mso-yfti-firstrow:yes'> | ||
<td width=40% valign=bottom align=left style='width:2.05in;padding:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt'> | <td width=40% valign=bottom align=left style='width:2.05in;padding:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt'> | ||
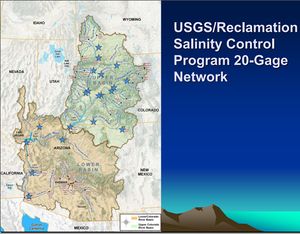
| − | <p class=MsoNormal>[[Image: | + | <p class=MsoNormal>[[Image:USGS-USBR- Salinity Control -20Gauge network.jpg|thumb|left|250px]]</p> |
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
------------Portal list on righthand side----------> | ------------Portal list on righthand side----------> | ||
|style="width:60%; font-size:95%;"| | |style="width:60%; font-size:95%;"| | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Water Quality - Colorado River''' |
| − | + | The quality of water in the Colorado River is important. Water quality includes, but not limited to, temperature, water column structure, total suspended solids, dissolved oxygen, total dissolved solids, and chlorophyll. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| Line 47: | Line 45: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | + | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Water Quality Links</h2> |
|- | |- | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| + | *'''General''' | ||
| + | *GCMRC Monitoring Stations Map | ||
| + | [http://www.gcmrc.gov/discharge_qw_sediment/stations/GCDAMP | ||
| + | GCMRC Maps and Spatial Data] | ||
| + | [http://www.gcmrc.gov/gis/silvermap1.aspx] | ||
| + | '''Temperature''' | ||
| − | == | + | *[http://waterdata.usgs.gov/az/nwis/uv/?site_no=09380000&PARAmeter_cd=00065,00060 USGS 09380000 COLORADO RIVER AT LEES FERRY, AZ] |
| − | + | *[http://waterdata.usgs.gov/usa/nwis/uv?09380000 USGS 09380000 COLORADO RIVER AT LEES FERRY, AZ] | |
| − | == | + | *[http://waterdata.usgs.gov/nv/nwis/uv/?site_no=09421500&PARAmeter_cd=00065,00060 USGS 09421500 COLORADO RV BLW HOOVER DAM, AZ-NV] |
| − | + | '''Salinity''' | |
| + | *'''[http://www.coloradoriversalinity.org/ Salinity Control Forum]'''[http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/national/programs/alphabetical/?cid=stelprdb1044198 Salinity Program Overview] | ||
| + | *[[Media:USCODE-2011-title43-chap32A-1.pdf |USCODE-2011-title43-chap32A-1.pdf -The codified version of the Colorado River Basin Salinity Control Act as amended. It includes both Title I and Title II. It also includes footnotes and history of amendments. ]] | ||
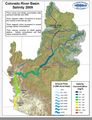
| − | == | + | == 2011 Water quality standards for salinity == |
| − | + | [http://coloradoriversalinity.org/docs/2011%20REVIEW-October.pdf] | |
| + | *Station ---------------- Salinity in mg/L | ||
| + | **Below Hoover Dam '''723''' | ||
| + | **Below Parker Dam '''747''' | ||
| + | **At Imperial Dam '''879''' | ||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | + | *'''Glen Canyon Dam''' | |
| + | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/05nov29/Attach_07.pdf USBR TWG Meeting] | ||
| − | ' | + | '''Lake Mead''' |
| − | + | *[http://www.nps.gov/lake/naturescience/water-quality-and-limnology.htm NPS Lake water quality and limnology] | |
| − | ''''' | + | |
| − | . | + | |
| − | + | *[http://nevada.usgs.gov/water/lmqw/map.htm Nevada USGS] | |
| − | . | + | *[http://www.ndep.nv.gov/forum/index.htm NDEP Lake Mead Water Quality Forum (NDEP)] |
| − | . | + | *[http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2010/1159/ HFE experiments on water quality (USGS)] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | *[http://az.water.usgs.gov/projects/LCRS/ Lower Colorado River Studies (USGS)] | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | *'''MONITORING HISTORY''' | ||
| + | # Water-quality sampling in Lake Powell was initiated by the USBR in 1964 and continued through 1990. | ||
| + | # Glen Canyon Environmental Studies conducted the monitoring from 1990-1996. | ||
| + | # The USGS Water Resources Discipline conducted monitoring in Lake Powell on several dates in 1992, 1994, and 1995. | ||
| + | # Since 1997, monitoring has been conducted by the USGS-GCMRC. | ||
| + | [http://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/1282/c1282.pdf State of the Colorado River Ecosystem in Grand Canyon- USGS Circular 1282] | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | *'''Additional Information'' | ||
| + | #[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/01apr12/Attach_08a.pdf "'''Cold water temperatures:''' Cold water temperatures suppress important diseases, parasites, competitors, and predators of native fish."(pg26)] | ||
| + | *Q: How could increases in salinity levels affect Lake Mead? | ||
| + | A: The associated costs might be felt from homeowners in the form of increases in corrosiveness to water fixtures/ pipes and more salt needed in the water softeners. | ||
| + | *Q: '''How do concentrations of salts (salinity) in the Colorado River cause economic damages to the Lower Basin?''' | ||
| + | *[Source: SNWA-CRC] The concentrations of salts in the Colorado River cause approximately $376 million in quantified damages in the Lower Basin each year and significantly more immeasurable damages. Modeling by the USBR indicates that quantifiable damages will rise to approximately $577 million per year by 2030 without the Salinity Control Program's continuation. | ||
| + | *Colorado River water increases from about '''50''' mg/L at its headwaters to more than '''700''' mg/L in the Lower Basin. High salt levels in the water cause significant economic damages downstream: | ||
| + | # a decrease in the life of treatment facilities and pipelines in the utility sector | ||
| + | # a reduction in the yield of salt-sensitive crops and increased water use to meet the leaching requirements in the agricultural sector | ||
| + | # increased use of imported water and cost of desalination and brine disposal for recycling water in the municipal sector | ||
| + | # a reduction in the useful life of galvanized water pipe systems, water heaters, faucets, garbage disposals, clothes washers and dishwaters, and increased use of bottled water and water softeners in the household | ||
| + | # an increase in the cost of cooling operations and the cost of water softening, and a decrease in equipment service life in the commercial sector | ||
| + | # an increase in the use of water and the cost of water treatment, and an increase in sewer fees in the industrial sector | ||
| + | # difficulty in meeting wastewater discharge requirements to comply with National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System permit terms and conditions, and an increase in deslination and brine disposal costs due to accumulation of salts in groundwater basins | ||
| + | |} | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Line 100: | Line 126: | ||
|class="MainPageBG" style="width:45%; border:1px solid #cedff2; background:#f5faff; vertical-align:top;"| | |class="MainPageBG" style="width:45%; border:1px solid #cedff2; background:#f5faff; vertical-align:top;"| | ||
{| width="100%" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="5" style="vertical-align:top; background:#f5faff;" | {| width="100%" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="5" style="vertical-align:top; background:#f5faff;" | ||
| − | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | + | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">News related LINKS</h2> |
|- | |- | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| − | * | + | *[[Media:201410 NDW Article Our Water Keeping it Clean.pdf |201410 NDW Article Our Water Keeping it Clean-- Green and Blue Algae]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
* | * | ||
* | * | ||
| Line 113: | Line 137: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| − | * | + | *[[Media:USBR-Las Vegas Wash 2012 Final Report- August 2014-PRINT.pdf |USBR-Las Vegas Wash 2012 Final Report- '''August 2014''']] |
| − | + | *[[Media:2014-47 40 Years Ago - The Genesis of the Salinity Control Program (1).pdf |2014-47 40 Years Ago - The Genesis of the Salinity Control Program]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | |
* | * | ||
| Line 125: | Line 147: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/01apr12/Attach_08a.pdf Example of '''surface water pump concept''' to change temperatures (pg13)] | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Image:Page 5.jpg | ||
| + | Image:20130227 Green River at Green River UT.jpg | ||
| + | Image:20130227 San Juan near Bluff.jpg | ||
| + | Image:20130227 Green River near Greendale.jpg | ||
| + | Image:20130227 White River near Watson.jpg | ||
| + | Image:20130227 San Rafael River near Green River.jpg | ||
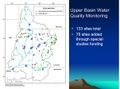
| + | Image:20130227 Upper Basin Water Quality Monitoring.jpg | ||
| + | Image:Diagram- USBR Colorado River Basin Salinity 09.jpg | ||
| + | Image:Temperature- pre and post dam- GRAPH.jpg | ||
| + | Image:Thermal Profiles in Lake Powell- Graph.jpg | ||
| + | Image:Turbidity USGS PIC.jpg | ||
| + | Image:150512 USGS-Water Quality MAP.jpg | ||
| + | Image:DIAGRAM- Turbidity and algae in Grand Canyon.jpg | ||
| + | Image:CRC_0014.JPG | ||
| + | Image:CRC_0015.JPG | ||
| + | Image:CRC_0016.JPG | ||
| + | Image:PIC- Water Quality CR NPS.jpg | ||
| + | Image:CRC_0018.JPG | ||
| + | Image:CRC_0019.JPG | ||
| + | Image:CRC_0020.JPG | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | *The river’s water quality varies as it travels through different stretches and land uses. Runoff from agriculture, abandoned mines, and naturally occurring saline ground water discharges cause localized water quality problems. | ||
| + | *ECONOMIC DAMAGES: (From Salinity) -- affected items include water heaters, washers, valves, faucets and the pipes themselves, and the costs of using more soap and softeners in laundry and dishwashers. Many plants are sensitive to salts around their roots, and high salinity water kills such plants. | ||
Latest revision as of 10:20, 24 November 2014
|
|
Water Quality - Colorado River The quality of water in the Colorado River is important. Water quality includes, but not limited to, temperature, water column structure, total suspended solids, dissolved oxygen, total dissolved solids, and chlorophyll.
|
| TBD (Motions) |
TBD (TBD) |
TBD (TBD) |
|---|
|
|