Difference between revisions of "Natal Origins Project (NO)"
From Glen Canyon Dam AMP
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|style="width:60%; font-size:120%;"| | |style="width:60%; font-size:120%;"| | ||
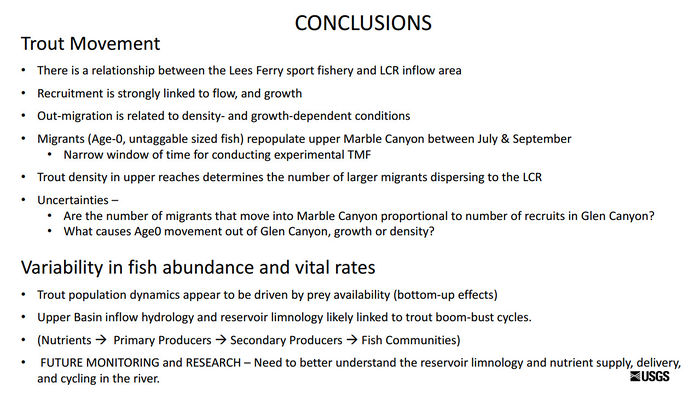
| − | *There is a low probability for an individual | + | *There is a low probability for an individual rainbow trout to move large distances. |
| − | *Abundance is a key factor: the more | + | *Abundance is a key factor: the more rainbow trout upstream in the Lees Ferry reach = more trout will move downstream to the LCR reach in search of unoccupied habitat |
| + | *Condition may be a secondary factor: when food resources become limited, rainbow trout will move downstream in search of food | ||
| + | *Recruitment in the reach below the LCR can be accounted for solely by immigrants from upstream sources | ||
| + | *Food limitation led to the collapse in the trout population, and by extension also likely happened in the downstream reaches. | ||
| + | *Inflow hydrology and reservoir limnology likely govern the quality and quantity of nutrients supplied to the downstream river segments. | ||
| + | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=Nutrients Nutrient limitation] is hypothesized as being the “BIG HAMMER” to the riverine ecosystem, which needs to be evaluated in greater detail in future research. [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf] | ||
|}<!-- | |}<!-- | ||
| Line 41: | Line 46: | ||
! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Updates</h2> | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Updates</h2> | ||
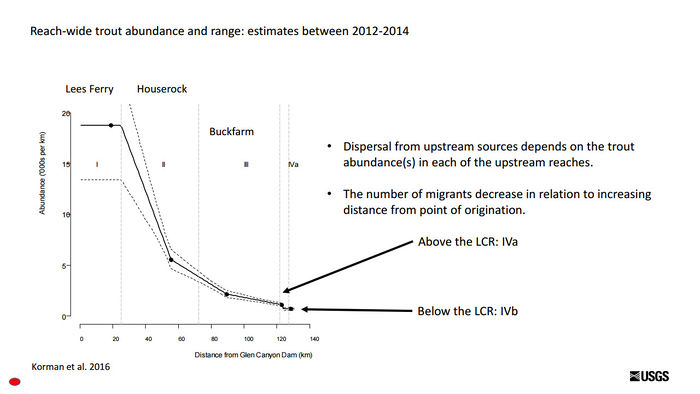
| − | [[File:ReachAbundances.jpg|center|700px | + | [[File:ReachAbundances.jpg|thumb|center|700px| [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf] ]] |
| − | [[File:EmigrationLargeRecruitmentEvents.jpg|center|700px | + | |
| − | [[File:EmigrationEnvironmentalStressor.jpg|center|700px | + | |
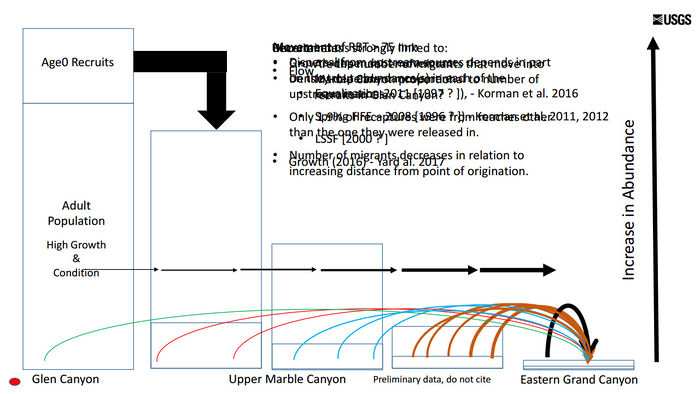
| − | [[File:NOconclusions.jpg|center|700px | + | [[File:EmigrationLargeRecruitmentEvents.jpg|thumb|center|700px| Episodic movement occurs under periods of high recruitment (lots of little trout looking for a place to live) |
| + | [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf] ]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
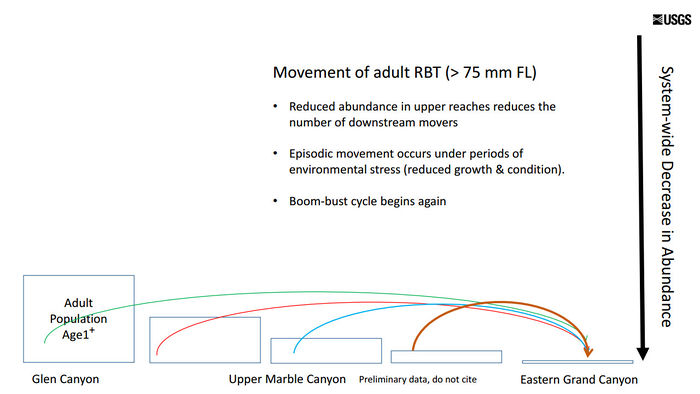
| + | [[File:EmigrationEnvironmentalStressor.jpg|thumb|center|700px| Episodic movement occurs under periods of environmental stress (poor conditions) [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf] ]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NOconclusions.jpg|thumb|center|700px| [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf] ]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 58: | Line 70: | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| − | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=FISHERY The | + | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=Bioenergetics_Studies Bioenergetics Studies] |
| − | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=Nutrients Nutrients Page] | + | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=FISHERY The Rainbow Trout Page] |
| + | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=Near_Shore_Ecology_(NSE)_Study The Near Shore Ecology (NSE) / Juvenile Chub Monitoring (JCM) Page] | ||
| + | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=Nutrients The Nutrients Page] | ||
|- | |- | ||
! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Background</h2> | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Background</h2> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 79: | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| − | + | Initial investigations found: | |
| − | *Efficacy of Mechanical Removal | + | *Efficacy of Mechanical Removal is dependent on immigration levels |
*RBT abundance was high and variable, partially offset by trout immigration | *RBT abundance was high and variable, partially offset by trout immigration | ||
*BNT were more predaceous than RBT | *BNT were more predaceous than RBT | ||
| Line 73: | Line 87: | ||
Information Needs: | Information Needs: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*What controls trout abundance? | *What controls trout abundance? | ||
*Where were RBT migrants originating from? | *Where were RBT migrants originating from? | ||
| Line 81: | Line 93: | ||
*Was there a relationship between HBC survival & RBT abundance? | *Was there a relationship between HBC survival & RBT abundance? | ||
| − | Outcomes: | + | Outcomes: <br> |
| − | + | Need to develop alternative sampling methods for determining trout and chub abundance and vital rates | |
| − | *Natal Origin Project: Movement and | + | *Natal Origin Project: Movement and trout dynamics |
*[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=Near_Shore_Ecology_(NSE)_Study NSE/JCM Projects]: Juvenile HBC survival and other regulating factors | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=Near_Shore_Ecology_(NSE)_Study NSE/JCM Projects]: Juvenile HBC survival and other regulating factors | ||
| Line 90: | Line 102: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''2018''' | ||
| + | *Yackulic, C.B., Korman, J., Yard, M.D., and J. Dzul.. 2018. Inferring species interactions through joint mark-recapture analysis. Ecology. Early view article. | ||
'''2017''' | '''2017''' | ||
| + | *Korman, J., M.D. Yard, and T.A. Kennedy. 2017. Trends in rainbow trout recruitment, abundance, survival, and growth during a boom-and-bust cycle in a tailwater fishery. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 146:1043-1057. | ||
| + | *Korman, J., and M.D. Yard. 2017. Effects of environmental covariates and density on the catchability of fish populations and the interpretation of catch per unit effort trends. Fish. Res. 189:18-34. | ||
| + | *Dzul, M.C., Yackulic, C.B., and J. Korman. 2017. Estimating disperser abundance using open population models that incorporate data from continuous detection PIT arrays. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. e-first article. | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR15_Korman.pdf Boom-and-Bust Cycles in the Population of Rainbow Trout in Glen Canyon and Effect of Fall High Flow Experiments ] | ||
*[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR16_Yard.pdf Natal Origin Project PPT] | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR16_Yard.pdf Natal Origin Project PPT] | ||
'''2016''' | '''2016''' | ||
| − | *[Natal Origins of Rainbow Trout Project, Years 1-4 (Nov 11 – Dec 15)] | + | *Yard, M.D., Korman, J., Walters, C.J., and T.A. Kennedy. 2016. Seasonal and spatial patters of growth of rainbow trout in the Colorado River in Grand Canyon Arizona. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 73:125-139. |
| + | *Korman, J, Yard, M.D., and C.B. Yackulic. 2016. Factors controlling the abundance of rainbow trout in the Colorado River in Grand Canyon in a reach utilized by endangered humpback chub. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 73:105-124. | ||
| + | *Dodrill, M.D., Yackulic, C.B., Yard, M.D. and J.W. Hayes. 2016. Prey size and availability limits maximum size of rainbow trout in a large tailwater: insights from a drift-foraging bioenergetics model. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 73: 759-772. | ||
| + | *Dzul, M.C., Yackulic, C.B., Korman, J., Yard, M.D., and J.D. Muehlbauer. 2016. Incorporating temporal heterogeneity in environmental conditions into a somatic growth model. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 74:316-326. | ||
| + | *Finch, C., W. E. Pine, C. B. Yackulic, M. J. Dodrill, M. Yard, B. S. Gerig, L. G. Coggins, and J. Korman. 2016. Assessing Juvenile Native Fish Demographic Responses to a Steady Flow Experiment in a Large Regulated River. River Research and Applications 32:763-775 | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/16jan26/index.html Natal Origins of Rainbow Trout Project, Years 1-4 (Nov 11 – Dec 15)] | ||
'''2015''' | '''2015''' | ||
| − | *[http://www. | + | *[http://www.nrcresearchpress.com/doi/abs/10.1139/cjfas-2015-0101#.WQOC9lXyu00 Korman et al. 2015. Factors controlling the abundance of rainbow trout in the Colorado River in Grand Canyon in a reach utilized by endangered humpback chub. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 2016, 73(1): 105-124] |
*[[2015 News about the declining fish status at Fishery| Update on the 2015 decline in fish condition and abundance at Lees Ferry]] | *[[2015 News about the declining fish status at Fishery| Update on the 2015 decline in fish condition and abundance at Lees Ferry]] | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2015-01-20-twg-meeting/Attach_12.pdf Natal Origins of Rainbow Trout: Glen Canyon and Marble Canyon] |
| − | + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2015-01-20-twg-meeting/Attach_18.pdf Rainbow Trout Growth, Condition, Population Dynamics and Modeling in Glen Canyon] | |
| − | *[ | + | |
'''2014''' | '''2014''' | ||
| − | * | + | *Yackulic, C.B, Yard, M.D., Korman, J. and D.R. Haverbeke. 2014. A quantitative life history of endangerd humpback chub that spawn in the Little Colorado River: variation in movement, growth, and survival. Ecol. Evol. 4: 1006-100. |
| − | + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2014-10-28-twg-meeting/Attach_12.pdf New Insights on Trout from the Natal Origins Study] | |
| − | *[ | + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2014-01-30-twg-meeting/AR_Yard_Korman_NO.pdf Natal Origins of Rainbow Trout: Glen Canyon and Marble Canyon] |
| − | *[ | + | |
'''2013''' | '''2013''' | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2013-01-24-twg-meeting/5_Yard.pdf Natal Origins: Glen Canyon and Marble Canyon] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 124: | Line 140: | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
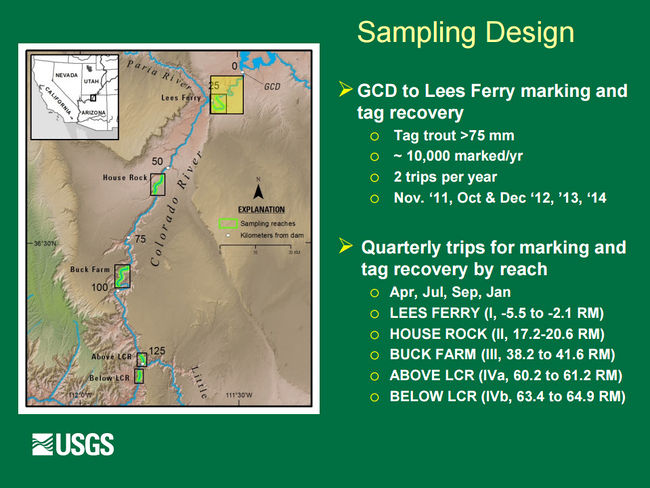
| + | [[File:NatalOriginsSamplingDesign_(1).jpg|center|650px]] | ||
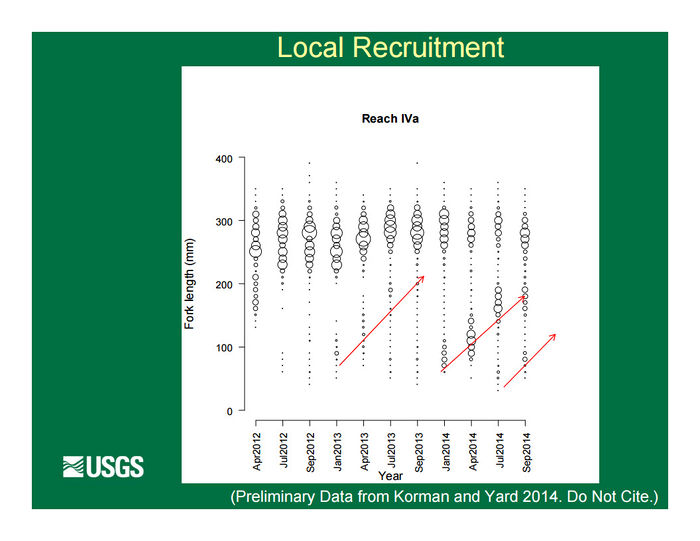
| + | =='''Local recruitment in Marble Canyon down to the LCR:'''== | ||
| + | There does appear to be some local trout recruitment in Marble Canyon down to the LCR but the numbers of trout at the LCR are driven more by immigration from upstream sources (i.e. the Lees Ferry reach) than by local recruitment. [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2014-10-28-twg-meeting/Attach_12.pdf] [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2017-01-26-twg-meeting/AR16_Yard.pdf] [[File:LocalRecruitment.jpg|center|700px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:43, 23 January 2019
|
|
|
| -- |
-- |
-- |
|---|
|
|