Difference between revisions of "FISH"
(link Standardized Methods for Grand Canyon Fisheries Research 2012) |
(add more detail) |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
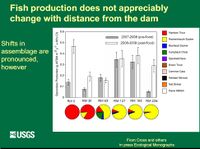
[[File:Fish production does not appreciably change with distance from the dam Slide 24.jpg |200px]] | [[File:Fish production does not appreciably change with distance from the dam Slide 24.jpg |200px]] | ||
| − | *'''NON-NATIVE FISH HISTORY''' Non-native fish species present in Grand Canyon were mostly established as a result of intentional stocking to develop sport fisheries in the Colorado River and its trivutaries during the late 1800s and early 1900s. Impacts of these actions was not fully understood until later in the 20th Cetury when a shift to native species conservation management occurred in the NPS. Negative impacts of non-native fish and altered habitats on native fish species has been well-documented throughtout the world. '''Over 20 | + | *'''NON-NATIVE FISH HISTORY''' Non-native fish species present in Grand Canyon were mostly established as a result of intentional stocking to develop sport fisheries in the Colorado River and its trivutaries during the late 1800s and early 1900s. Impacts of these actions was not fully understood until later in the 20th Cetury when a shift to native species conservation management occurred in the NPS. Negative impacts of non-native fish and altered habitats on native fish species has been well-documented throughtout the world. '''Over 20 non-native fish species''' have been documented in GCNP; However, the more common, large-bodied, species of management concern include rainbow and brown trout, common carp, channel catfish, and bullhead species, striped and smallmouth bass. These species are known predators on native fish or native fish eggs or compete with native fish species.(NPS CFMP-EA_Pg 62) (17 warmwater species, 2 coldwater species, and 1 coolwater species)--- At least '''7''' additional species occur in nearby or adjoining waters with potential access to the Glen Canyon Ecosystem. |
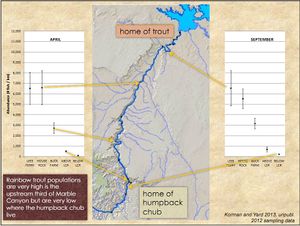
*The fish community throughout Marble Canyon, downstream of the Glen Canyon Reach is GCNP, is dominated by non-native rainbow trout. The fish community changes near the LCR inflow near RM 60 where native species begin to occur. (NPS CFMP-EA_Pg 63) | *The fish community throughout Marble Canyon, downstream of the Glen Canyon Reach is GCNP, is dominated by non-native rainbow trout. The fish community changes near the LCR inflow near RM 60 where native species begin to occur. (NPS CFMP-EA_Pg 63) | ||
Revision as of 14:30, 11 July 2013
|
Description The Colorado River running through Grand Canyon once hosted one of the most distinctive fish assemblages in North America. The wild Colorado River presented fish with a challenging and variable aquatic habitat: very large spring floods, near-freezing winter temperatures, warm summer temperatures, and a heavy silt load. Note that only eight fish species were native to Grand Canyon. Of the eight species, six are endemic, meaning that they are only found in the Colorado River basin. (NPS)
|
| TBD (Motions) |
TBD (TBD) |
TBD (TBD) |
|---|
|
LINK: usbr/amp/amwg/mtgs/13feb20/Attach_07b||| |