Difference between revisions of "FISH"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
----------Strapline immediately below banner----------> | ----------Strapline immediately below banner----------> | ||
{| style="width:100%; height:50px" border=1px solid #ccc; background:#cedff2 | {| style="width:100%; height:50px" border=1px solid #ccc; background:#cedff2 | ||
| − | ! style="width=33%; background:#cedff2;" | | + | ! style="width=33%; background:#cedff2;" | Fish Species of the Colorado River in Lower Glen Canyon and Grand Canyon| http://gcdamp.com/images_gcdamp_com/7/7a/140619_FISH_IN_RIVER_GCDAMPwiki-_AZGF.PDF |
| − | ! style="width=33%; background:#cedff2;" | [[TBD| | + | ! style="width=33%; background:#cedff2;" | [[TBD|--]] |
| − | + | ! style="width=33%; background:#cedff2;" | [[TBD|--]] | |
| − | ! style="width=33%; background:#cedff2;" | [[TBD| | + | |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 11:40, 31 May 2016
|
|
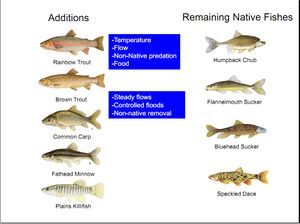
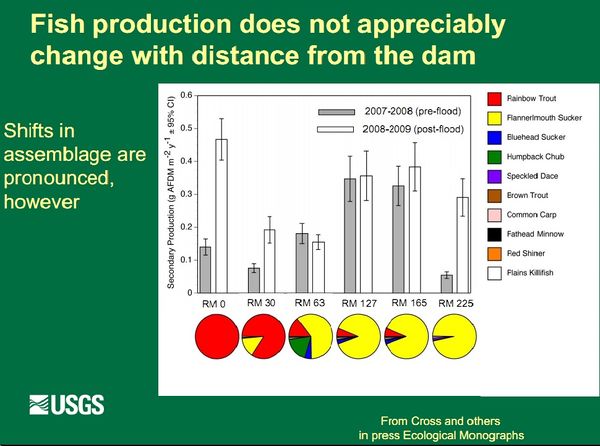
Grand Canyon was once home to eight species of native fish. Only five of these species are found in the park today. Following the completion of Glen Canyon Dam in 1963, the fish assemblage in the Colorado River in Grand Canyon has shifted to non-native rainbow and brown trout in the stretches of river closest to the dam and above the Little Colorado River. Of the canyon's native fish species, only speckled dace remain truly common in the park, and they live primarily in tributaries which retain their natural characteristics more than the Colorado River. Two species of Grand Canyon's native fish are listed under the Endangered Species Act. Humpback chub, which used to be abundant in Grand Canyon, has been listed as an endangered species since 1967. Razorback suckers are very rare in the canyon, and were listed as endangered in 1991. Grand Canyon has a very distinctive collection of native fish. All eight native species belong to only two families: minnows (Cyprinidae) and suckers (Catostomidae). Six of the eight native species are found only in the Colorado River basin. This very high percentage of endemic fish species likely results from the geographic isolation of the Colorado River system, and the highly variable natural environments, flow and temperature regimes of the river and its tributaries. The Colorado River has the lowest diversity of native fish and the highest level of endemism of any river system in North America. The river's unusual native fish assemblage is as iconic a characteristic of Grand Canyon as its towering cliffs, other endemic species such as the Grand Canyon rattlesnake, and spectacular scenery. |
| Fish Species of the Colorado River in Lower Glen Canyon and Grand Canyon| http://gcdamp.com/images_gcdamp_com/7/7a/140619_FISH_IN_RIVER_GCDAMPwiki-_AZGF.PDF | -- | -- |
|---|
NON-NATIVE FISH HISTORY Non-native fish species present in Grand Canyon were mostly established as a result of intentional stocking to develop sport fisheries in the Colorado River and its tributaries during the late 1800s and early 1900s. Impacts of these actions was not fully understood until later in the 20th Century when a shift to native species conservation management occurred in the NPS. Negative impacts of non-native fish and altered habitats on native fish species has been well-documented throughtout the world. Over 20 non-native fish species have been documented in GCNP; However, the more common, large-bodied, species of management concern include rainbow and brown trout, common carp, channel catfish, and bullhead species, striped and smallmouth bass. These species are known predators on native fish or native fish eggs or compete with native fish species.(NPS CFMP-EA_Pg 62) (17 warmwater species, 2 coldwater species, and 1 coolwater species)--- At least 7 additional species occur in nearby or adjoining waters with potential access to the Glen Canyon Ecosystem.
|
|