Difference between revisions of "Nutrients"
From Glen Canyon Dam AMP
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''2018''' | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/18jan25/AR11.pdf Temperature and nutrients as ecosystem drivers in the Colorado River PPT, Lake Powell as a regulator of temperature and Lake Powell as a regulator of nutrients PPT] | ||
'''2017''' | '''2017''' | ||
Revision as of 16:50, 27 March 2018
|
|
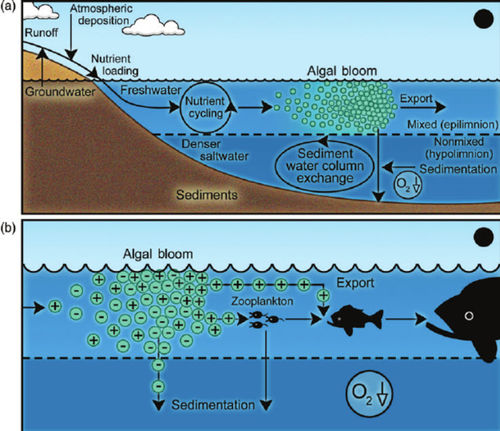
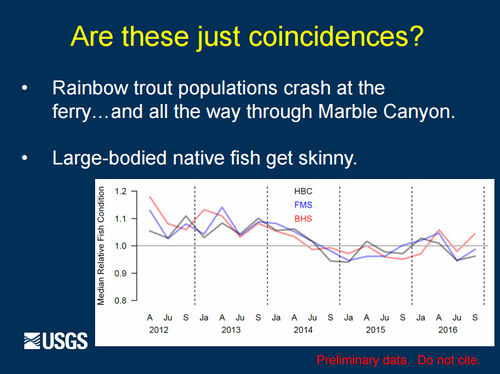
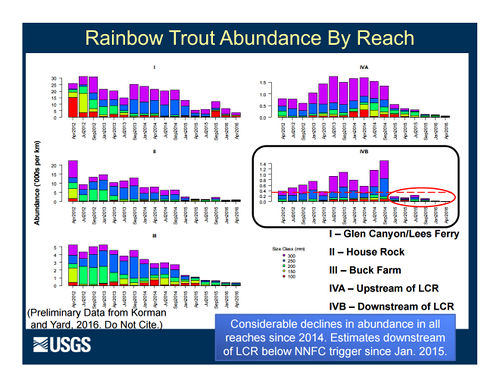
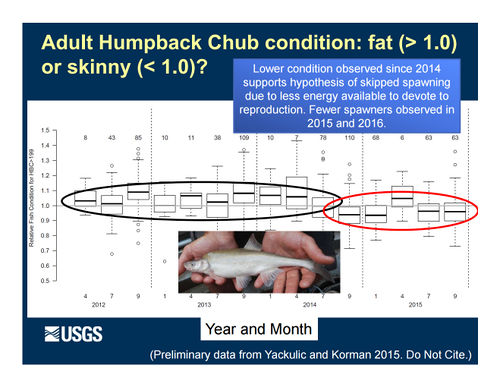
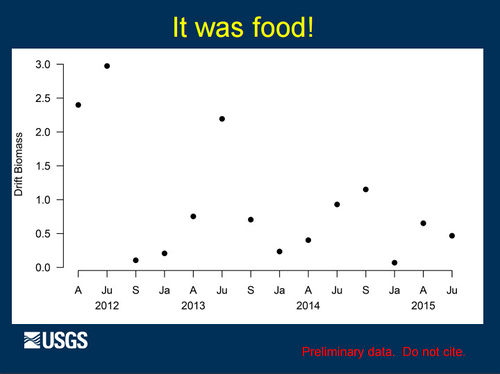
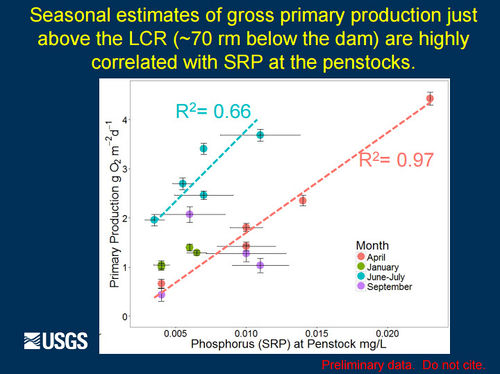
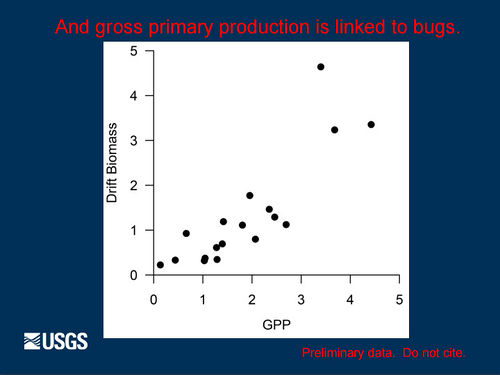
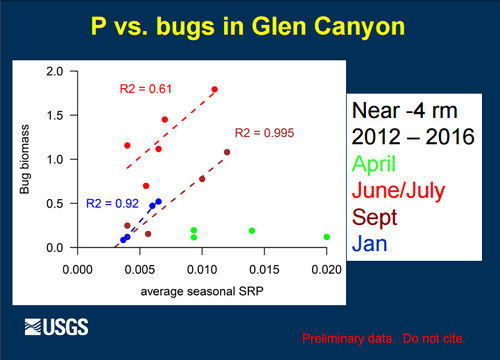
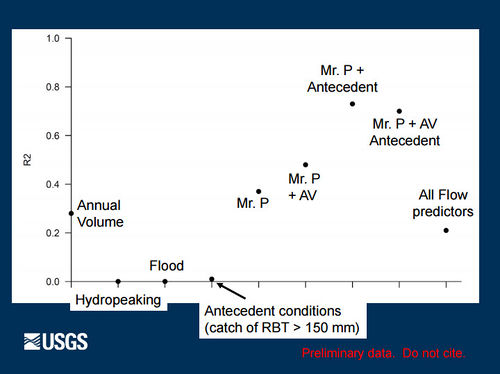
Role of Nutrients in Fish Population Dynamics below Glen Canyon DamThe 2012-2014 rainbow trout population decline corresponded with a decline in condition for other large-bodied native fish like humpback chub, flannelmouth sucker, and bluehead sucker. These declines in fish population size and body condition occurred at the same time as a decline in drift biomass in the foodbase below Glen Canyon Dam. Primary production in the Colorado River is nutrient limited (soluble reactive phosphorous or SRP). Seasonal estimates of primary production just above the LCR are highly correlated with SRP measured at the Glen Canyon Dam. Primary production is linked to foodbase production, native fish condition, and rainbow trout condition and recruitment. [1] |
| --- |
--- |
--- |
|---|
|
|