Difference between revisions of "HYDROPOWER"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| − | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/crsp/gc/ | + | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/crsp/gc/index.html '''U.S. Bureau of Reclamation (USBR)'''] |
*'''[https://www.wapa.gov/Pages/western.aspx Western Area Power Administration (WAPA)]''' | *'''[https://www.wapa.gov/Pages/western.aspx Western Area Power Administration (WAPA)]''' | ||
*'''[http://www.creda.org/ Colorado River Energy Distribution Association (CREDA)]''' | *'''[http://www.creda.org/ Colorado River Energy Distribution Association (CREDA)]''' | ||
Revision as of 16:24, 2 June 2016
 Fly Around Video Clip of Generating Unit Fly Around Video Clip of Generating Unit
|
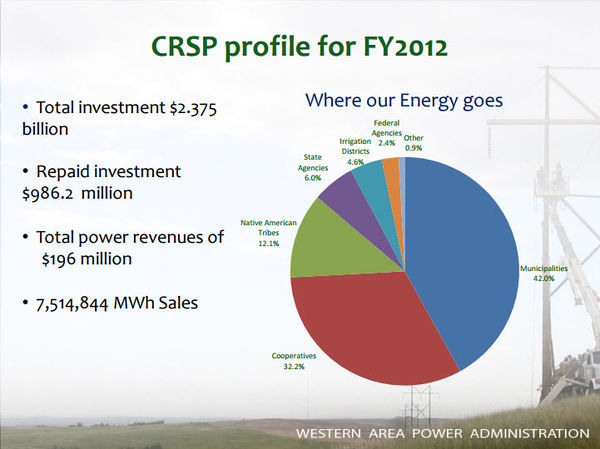
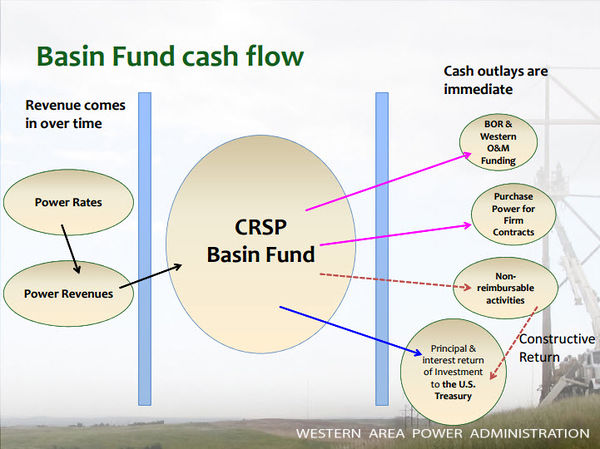
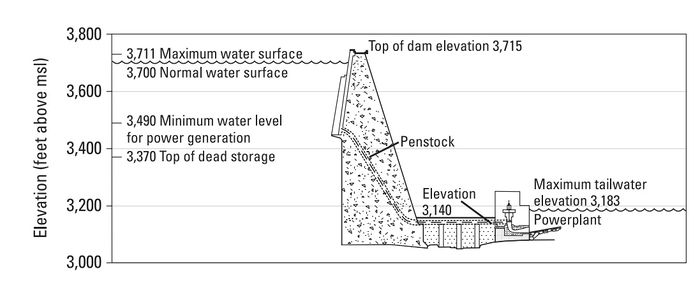
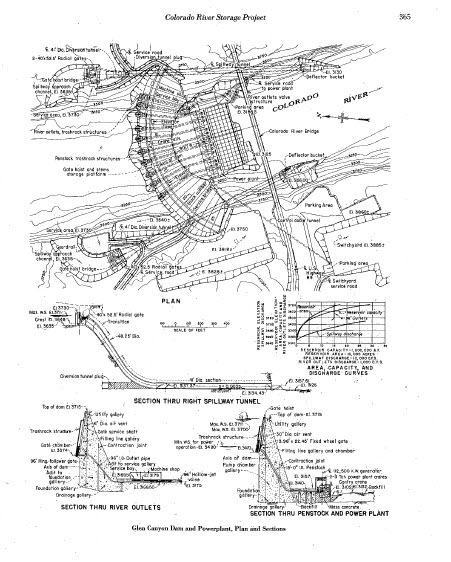
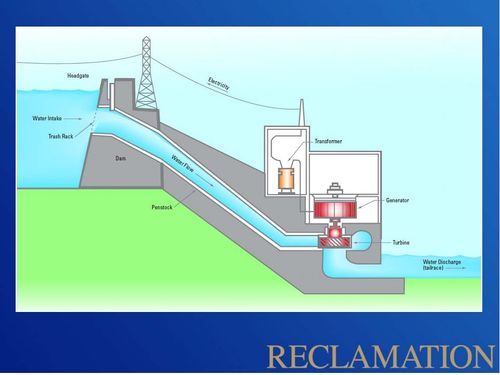
Glen Canyon Dam is a 710-foot-high concrete arch dam, and the second highest dam in the United States. The powerplant at Glen Canyon Dam is made up of eight hydroelectric generation stations. The combined generation capability of all eight turbines is 1,320 megawatts. The hydropower resource at Glen Canyon Dam is monitored intensively by the Bureau of Reclamation and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Western Area Power Administration (WAPA), the entity that markets Glen Canyon Dam power to power distributors in the western United States. Tracking power generation, power market rates, necessary power purchases, and power revenue provides a mechanism for understanding how changes in Glen Canyon Dam operations affect energy generation and the energy market. |
| --- |
--- |
--- |
|---|
|
|