Difference between revisions of "Humpback Chub Page"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
'''2016''' | '''2016''' | ||
| − | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/16aug24/Attach_07a.pdf | + | *[http://blog.nature.org/science/2016/10/25/recovery-humpback-chubs-new-values-and-new-hope-for-endangered-native-fish/ Recovery: Humpback Chubs, New Values and New Hope for Endangered Native Fish] |
| − | *[[Media:HBC Monitoring above Lower Atomizer Falls 2016 Trip Report.pdf Spring 2016 Chute Falls humpback chub sampling trip report]] | + | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/16aug24/Attach_07a.pdf Grand Canyon Monitoring and Research Center Science Updates (BO Compliance, Trout Updates, Green Sunfish, Fisheries PEP, Partners in Science)] |
| − | *[[Media:Lower LCR Spring 2016 Trip Report.pdf Spring 2016 Lower LCR humpback chub sampling trip report]] | + | *[[Media:HBC Monitoring above Lower Atomizer Falls 2016 Trip Report.pdf| Spring 2016 Chute Falls humpback chub sampling trip report]] |
| − | *[[Media:2016 VanHaverbeke HBC LCR.pdf Mark-Recapture and Fish Monitoring Activities in the Little Colorado River in Grand Canyon Colorado River in Grand Canyon from 2000 to 2015]] | + | *[[Media:Lower LCR Spring 2016 Trip Report.pdf| Spring 2016 Lower LCR humpback chub sampling trip report]] |
| + | *[[Media:2016 VanHaverbeke HBC LCR.pdf| Mark-Recapture and Fish Monitoring Activities in the Little Colorado River in Grand Canyon Colorado River in Grand Canyon from 2000 to 2015]] | ||
*[http://fwspubs.org/doi/pdf/10.3996/102015-JFWM-101 Effects of Turbidity on Predation Vulnerability of Juvenile Humpback Chub to Rainbow and Brown Trout] | *[http://fwspubs.org/doi/pdf/10.3996/102015-JFWM-101 Effects of Turbidity on Predation Vulnerability of Juvenile Humpback Chub to Rainbow and Brown Trout] | ||
*[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/16jan26/documents/Attach_01.pdf Recovery Plan update for Humpback Chub] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/16jan26/documents/Attach_01.pdf Recovery Plan update for Humpback Chub] | ||
| Line 137: | Line 138: | ||
'''2015''' | '''2015''' | ||
| + | *[[Media:Finch et al 2015 FSSchubGrowth.pdf| Finch, C., W.E. Pine III, C.B. Yackulic, M.J. Dodrill, M. Yard, B.S. Gerig, L.G. Coggins, Jr., and J. Korman, 2015, “Assessing Juvenile Native Fish Demographic Responses to a Steady Flow Experiment in a Large Regulated River,” River Research and Applications. doi:10.1002/rra.2893.]] | ||
*[https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BwY-Z2c3NTUGdXc2WHJOWkdBX3M/view Havasu Creek Translocation Update] | *[https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BwY-Z2c3NTUGdXc2WHJOWkdBX3M/view Havasu Creek Translocation Update] | ||
*[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/15feb25/Attach_05b.pdf Native-nonnative Interactions; Factors Influencing Predation and Competition] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/15feb25/Attach_05b.pdf Native-nonnative Interactions; Factors Influencing Predation and Competition] | ||
| Line 150: | Line 152: | ||
*[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14oct28/Attach_13.pdf Modeling Long Term Effects of HFEs on Trout and HBC] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14oct28/Attach_13.pdf Modeling Long Term Effects of HFEs on Trout and HBC] | ||
*[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/14aug27/index.html Factors Influencing Humpback Chub Population Dynamics ] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/14aug27/index.html Factors Influencing Humpback Chub Population Dynamics ] | ||
| − | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/14aug27/Attach_04a.pdf | + | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/14aug27/Attach_04a.pdf Science Updates - Recent Research on Sand, Bugs, and Fish ] |
*[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14jan30/AR_Persons_Fish_monitoring.pdf Colorado River fish monitoring in Grand Canyon, Arizona: 1990-2013 humpback chub, Gila cypha, aggregations] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14jan30/AR_Persons_Fish_monitoring.pdf Colorado River fish monitoring in Grand Canyon, Arizona: 1990-2013 humpback chub, Gila cypha, aggregations] | ||
*[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14jan30/AR_Yackulic_Results.pdf Results from Colorado River Site and ongoing population modeling] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14jan30/AR_Yackulic_Results.pdf Results from Colorado River Site and ongoing population modeling] | ||
Revision as of 09:01, 28 October 2016
|
DescriptionThe humpback chub (Gila cypha) is an endangered, native endemic of the Colorado River that evolved around 3-5 million years ago. The pronounced hump behind its head gives this fish a striking, unusual appearance. It has an olive-colored back, silver sides, a white belly, small eyes and a long snout that overhangs its jaw. Like the Colorado pikeminnow and bonytail, the humpback chub is a member of the minnow family. The humpback chub is a relatively small fish by most standards – its maximum size is about 20 inches and 2.5 pounds. By minnow standards it is a big fish, though not like the giant of all minnows – the Colorado pikeminnow. Humpback chub can survive more than 30 years in the wild. It can spawn as young as 2 to 3 years of age during its March through July spawning season. Although the humpback chub does not have the swimming speed or strength of the Colorado pikeminnow, its body is uniquely formed to help it survive in its whitewater habitat. The hump that gives this fish its name acts as a stabilizer and a hydrodynamic foil that helps it maintain position and also probably helped it escape predation by making it difficult to be swallowed by all but the largest pikeminnow. The humpback chub uses its large fins to “glide” in eddy complexes, feeding on insects that become trapped in pockets of slow-moving water. Status and distribution
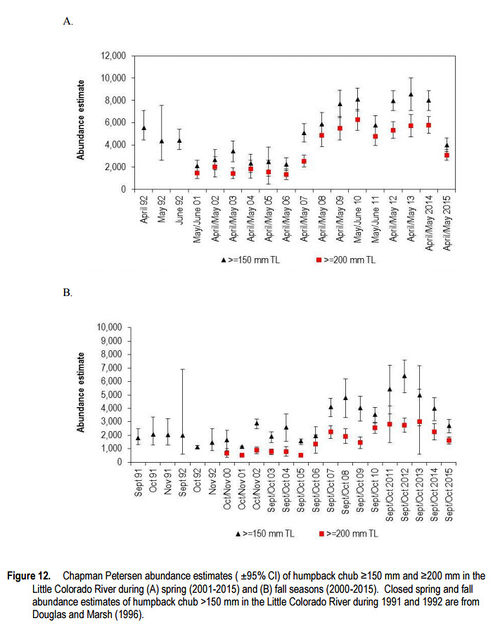
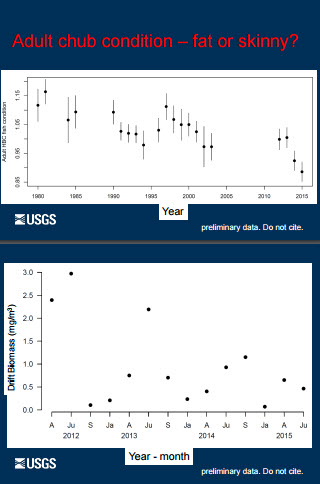
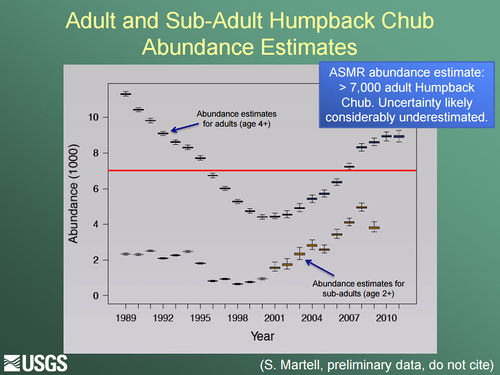
The humpback chub was listed as endangered by U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service in 1967 and given full protection under the Endangered Species Act of 1973. Historically, humpback chub were probably limited to the eddy complexes of several canyon reaches of the Colorado River and three of its tributaries: the Green and Yampa rivers in Colorado and Utah, and the Little Colorado River in Arizona. The species was first described in 1946. Before that time, few people ventured into these treacherous canyons – including fishery biologists. Today, five self-sustaining populations of humpback chub occur in the Upper Colorado River Basin. Two to three thousand adults can occur in the Black Rocks and Westwater Canyon core population in the Colorado River near the Colorado/Utah border. Several hundred to more than 1,000 adults may occur in the Desolation/Gray Canyon core population in the Green River. Populations in Yampa and Cataract canyons are small, each consisting of up to a few hundred adults. The largest population of humpback chub is found in the Grand Canyon -- primarily in the Little Colorado River (LCR) and its confluence with the main stem Colorado River. In 2009, the U.S. Geological Survey announced that this population increased by about 50 percent from 2001 to 2008 to between 6,000 and 10,000 adults. One of the primary threats to humpback chub has been the proliferation of warm-water nonnative fish predators like smallmouth bass and northern pike. Desired Future Condition for Humpback Chub• Achieve HBC recovery in accord with the Endangered Species Act (ESA), the HBC comprehensive management plan, and with the assistance of collaborators within and external to the AMP. |
| --- | Fish Species of the Colorado River in Lower Glen Canyon and Grand Canyon 
|
--- |
|---|