Difference between revisions of "Natal Origins Project (NO)"
From Glen Canyon Dam AMP
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
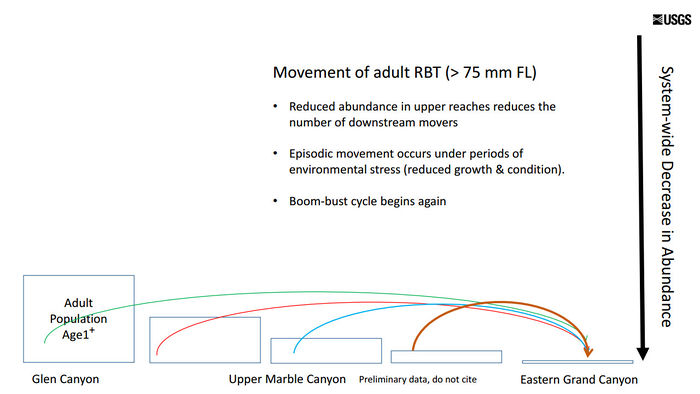
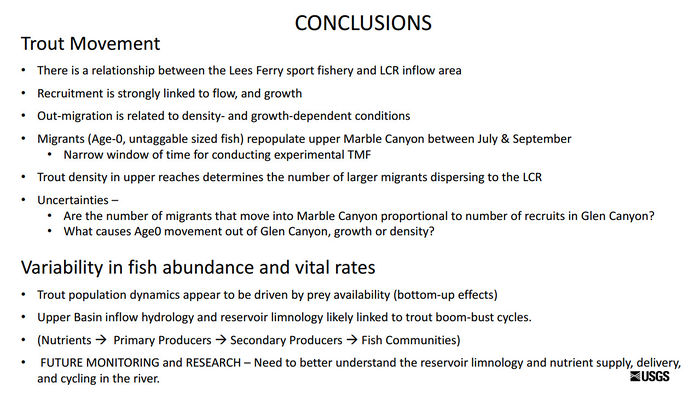
*There is a low probability for an individual fish to move large distances. | *There is a low probability for an individual fish to move large distances. | ||
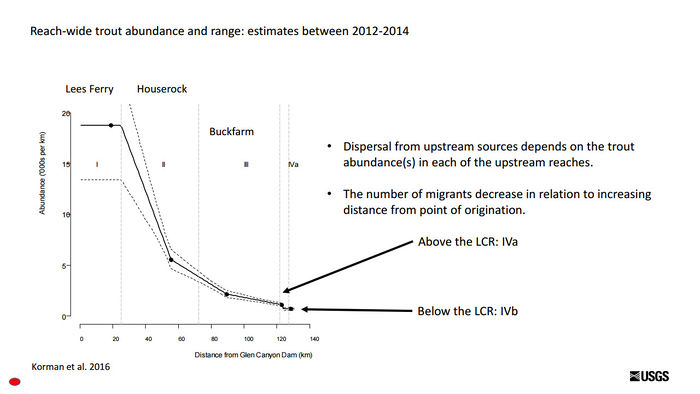
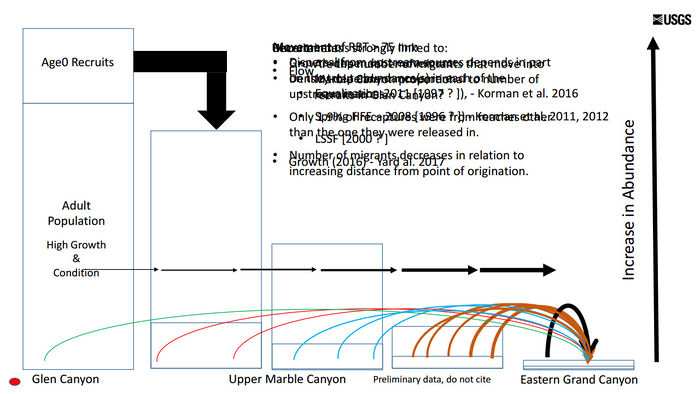
*Abundance is a key factor: the more fish upstream in the Lees Ferry reach = more fish will move downstream | *Abundance is a key factor: the more fish upstream in the Lees Ferry reach = more fish will move downstream | ||
| + | *Recruitment in the reach below the LCR can be accounted for solely by immigrants from upstream sources (little to no local recruitment at the LCR) | ||
| + | *Food limitation lead to the collapse in the trout population, and by extension also likely happened in the downstream reaches. | ||
| + | *Inflow hydrology and reservoir limnology likely govern the quality and quantity of nutrients supplied to the downstream river segments. | ||
| + | *Nutrient limitation is hypothesized as being the “BIG HAMMER” to the riverine ecosystem, which needs to be evaluated in greater detail in future research. | ||
|}<!-- | |}<!-- | ||
Revision as of 16:25, 26 April 2017
|
|
|
| -- |
-- |
-- |
|---|
|
|