|
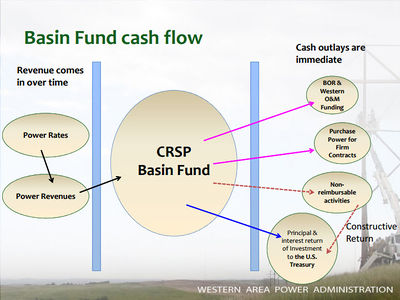
Basin Fund revenues must first be used to repay costs associated with the operation, maintenance, and replacements of, and emergency expenditures for, the CRSP initial units. The fund is then used to repay the United States Treasury Department for the following:
- The construction costs of the CRSP initial units allocated to the power purpose (with interest thereon)
- The construction costs of the CRSP initial units allocated to irrigation
- A portion of salinity investment and operation costs
- The construction costs of the participating projects allocated to the irrigation investment and above the irrigator's ability to pay
The Basin Fund also supports the following:
- Cost sharing for Colorado River Basin Salinity Control Program (approximately $2.0 million annually)
- The major portion of the cost of the Glen Canyon Adaptive Management Program (currently almost $9.5 million annually)
- Cost sharing for the Upper Colorado and San Juan Endangered Fish Recovery Implementation Programs (currently approximately $7 million annually)
- Water quality studies
- Consumptive use studies
The approximately $16.5 million per year of power revenues expended for the Glen Canyon Adaptive Management Program, the Upper Colorado River Recovery Implementation Program, and the San Juan Basin Recovery Program are expenses that are not built into the firm power rates. This arrangement benefits the programs in that they do not need to seek annual appropriations from Congress for these funds. However, this does have an impact to Western in times when firming power purchase expenses are high (due to drought or experimentation) because the moneys are transferred to the program and are not available to purchase the power needed to meet contractual requirements. The Basin Fund is managed by Western. Approximately $120 million in revenue is needed each year to fund Reclamation and Western operation and maintenance needs. Western is responsible for transmission and marketing of CRSP power, collecting payment for the power, and transfer of revenues for repayment to the United States Treasury Department. A change in the amount of available capacity or energy could potentially affect the revenue derived from the sale of energy and the contributions to the Basin Fund, or rates charged to power customers. [2]
How are the costs associated with experimentation and the environmental programs paid for?
- Costs incurred during experimentation, like funding dedicated to environmental programs, are booked as a non-reimbursable activity.
- This means they can be booked as a constructive return (i.e. in lieu of an actual cash return) to the U.S. Treasury as a payment against the loan that was taken out to construct the CRPS units.
- The amount WAPA returns to the Treasury for the construction of the CRSP units is finite and scheduled.
- As the amount WAPA needs to return to the Treasury gets smaller, the amount of interest incorporated in the return also gets smaller.
- As these amounts gets smaller over time, it reduces the amount WAPA can claim as a non-reimbursable return.
- Over time, this reduces the amount of funding available for non-reimbursable activities like experimentation and environmental programs.
What happens if the amount in the Basin Fund falls below the amount necessary to purchase power for firm contracts?
Some combination of the following:
- Increase power rates through a CRC (Cost Recovery Charge)
- Increase power revenues through a re-operation of the CRSP facilities (i.e. relax environmental restrictions)
- Reduce BOR and WAPA O&M funding
- Reduce allocations for firm power contracts
- Reduce funding for non-reimbursable activities
How has re-operation at Glen Canyon Dam affected power revenues?
- 1996 EIS and MLFF
- 2016 LTEMP EIS [3]
How much does the Federal Government make off of power revenues at Glen Canyon Dam?
- None
- Legislation requires full cost recovery, meaning, total revenue equals total costs. Profits are not allowed.
- Total annual revenue and costs for the SLCA/IP is about $200 million/year [4]
|