HYDROPOWER
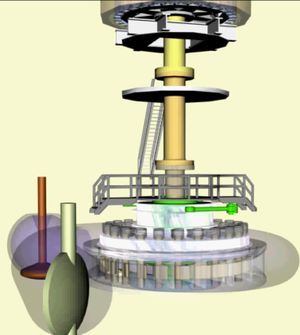 Fly Around Video Clip of Generating Unit Fly Around Video Clip of Generating Unit
|
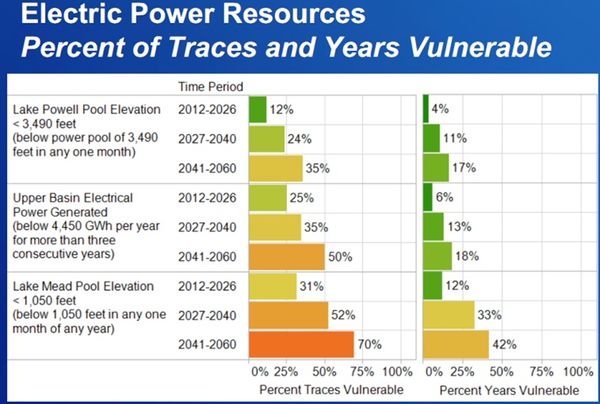
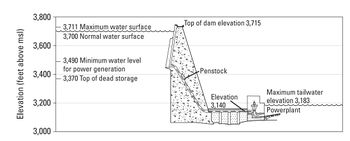
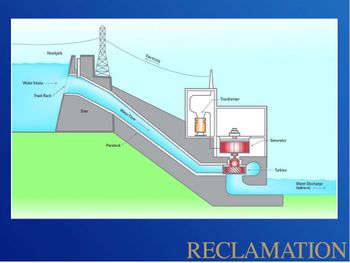
HYDROPOWER GCMRC definition link Power production is included under GCMRC Science activities because minimizing impacts to power production is one of the goals of the Glen Canyon Dam Adaptive Management Program, therefore systematic monitoring and focused research is needed to determine how changes in dam operations to meet various environmental objectives may affect the availability and value of hydropower. Glen Dam is a 710-foot-high concrete arch dam, and the second highest dam in the United States. The powerplant at Glen Canyon Dam is made up of eight hydroelectric generation stations. The combined generation capability of all eight turbines is 1,320.0 megawatts. Glen Canyon Dam is a peaking power facility designed to rapidly change output levels in response to changes in demand for electricity. Although Glen Canyon Dam meets only a very small portion of the total energy demand in the western United States, it plays an important and valuable role in the region in terms of being able to respond rapidly to changing power demands throughout the western electrical grid. The hydropower resource at Glen Canyon Dam is monitored intensively by the Bureau of Reclamation and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Western Area Power Administration (WAPA), the entity that markets Glen Canyon Dam power to rural power distributors in the western United States. Tracking power generation, power market rates, necessary power purchases, and power revenue provides a mechanism for understanding how changes in Glen Canyon Dam operations affect energy generation and the energy market. In the near future, GCMRC intends to provide links through this web site to hourly data on energy generation, Basin Fund balances, monthly energy purchases, and other data routinely compiled by WAPA. In addition, GCMRC works with WAPA economists and energy system modelers to provide retrospective and predictive evaluations of the economic implications to hydropower from changing dam operations to meet environmental objectives of the Glen Canyon Dam Adaptive Management Program. |
| --- |
--- |
--- |
|---|
|
|