|
|
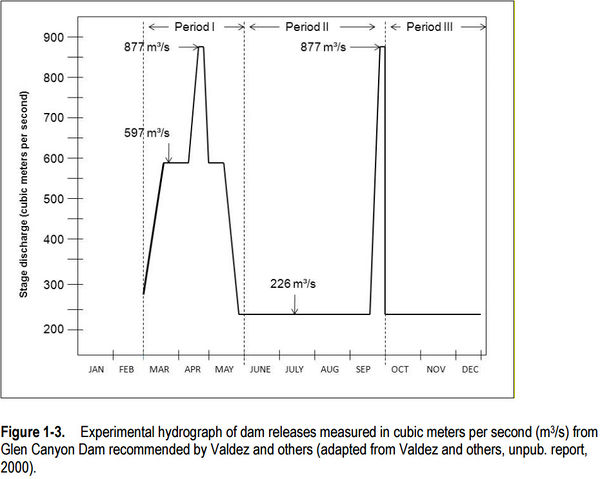
In the spring and summer of 2000, a series of steady discharges of water from Glen Canyon Dam on the Colorado River were used to evaluate the effects of aquatic habitat stability and water temperatures on native fish growth and survival, with a special focus on the endangered humpback chub (Gila cypha), downstream from the dam in Grand Canyon. The steady releases were bracketed by peak powerplant releases in late-May and early-September. The duration and volume of releases from the dam varied between spring and summer. The intent of the experimental hydrograph was to mimic predam river discharge patterns by including a high, steady discharge in the spring and a low, steady discharge in the summer. The hydrologic experiment was called the Low Steady Summer Flow (LSSF) experiment because steady discharges of 226 m3/s dominated the hydrograph for 4 months from June through September 2000.
The experimental hydrograph was developed in response to one of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service’s Reasonable and Prudent Alternatives (RPA) in its Biological Opinion of the Operation of Glen Canyon Dam Final Environmental Impact Statement. The RPA focused on the hypothesis that seasonally adjusted steady flows were dam operations that might benefit humpback chub more than the Record of Decision operations, known as Modified Low Fluctuating Flow (MLFF) operations. Condensed timelines between planning and implementation (2 months) of the experiment and the time required for logistics, purchasing, and contracting resulted in limited data collection during the high-release part of the experiment that occurred in spring. The LSSF experiment is the longest planned hydrograph that departed from the MLFF operations since Record of Decision operations began in 1996.
|
