Difference between revisions of "FOOD BASE"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
2016 | 2016 | ||
| − | *'''[[File:Kennedy 2016 HydropowerEPT.pdf | + | *'''[[File:Kennedy 2016 HydropowerEPT.pdf]]''' |
*'''[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/16jan26/documents/AR16_Muehlbauer.pdf Food availability in the Little Colorado River over space and time]''' | *'''[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/16jan26/documents/AR16_Muehlbauer.pdf Food availability in the Little Colorado River over space and time]''' | ||
*'''A Life History Bottleneck for Aquatic Insects Arising from Load Following''' | *'''A Life History Bottleneck for Aquatic Insects Arising from Load Following''' | ||
Revision as of 12:35, 25 May 2016
|
|
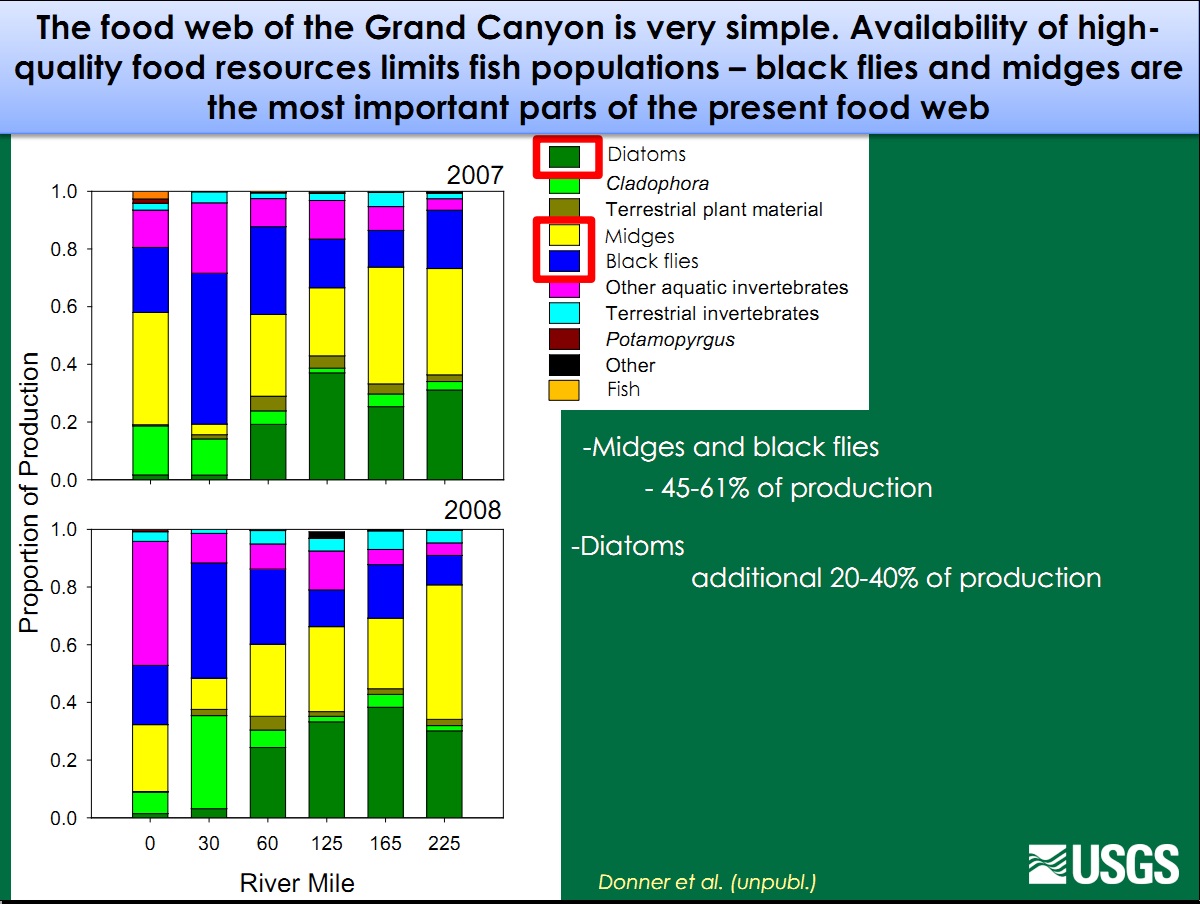
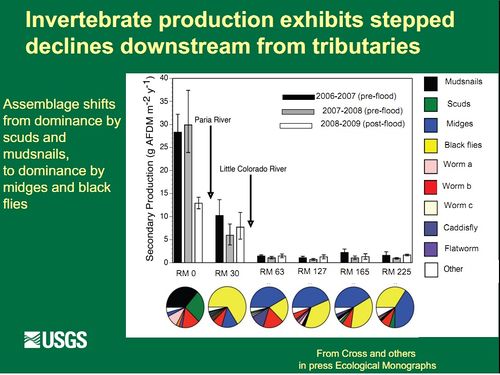
The Colorado River below Glen Canyon Dam has been altered by dam-induced modifications to the river’s flow, temperature, and sediment supply. Nonnative species have also changed the natural system. Nonnative fish are thought to prey on and compete with native fish, including the endangered humpback chub (Gila cypha). These impacts have likely changed both the amount and sources of energy that fuel the aquatic food web and the flows of energy within the food web. Installation of the dam created a relatively clear, cool aquatic environment below the dam that now allows aquatic plants to capture the sun’s energy, and they in turn are now consumed by a few species, including scuds (Gammarus lacustris), midges (Family: Chironomidae), blackflies (Simulium arcticum), and New Zealand mudsnails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). The first three species can provide food for both native and nonnative fishes, but fish cannot digest the New Zealand mudsnail. |
| TBD |
TBD |
TBD |
|---|