Difference between revisions of "GCDAMP Glen Canyon Dam"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Operational Flexibility </h2> | + | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Operational Flexibility </h2> |
|- | |- | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
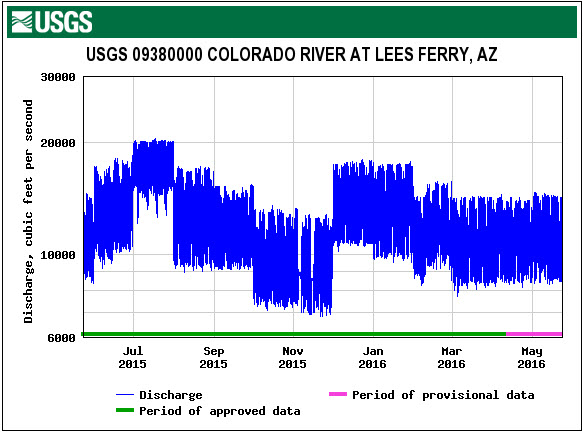
In addition to daily scheduled fluctuations for power generation, the instantaneous releases from Glen Canyon Dam may also fluctuate to provide 40 megawatts (mw) of system regulation. These instantaneous release adjustments stabilize the electrical generation and transmission system and translate to a range of about 1,200 cfs above or below the hourly scheduled release rate. Under system normal conditions, fluctuations for regulation are typically short lived and generally balance out over the hour with minimal or no noticeable impacts on downstream river flow conditions. | In addition to daily scheduled fluctuations for power generation, the instantaneous releases from Glen Canyon Dam may also fluctuate to provide 40 megawatts (mw) of system regulation. These instantaneous release adjustments stabilize the electrical generation and transmission system and translate to a range of about 1,200 cfs above or below the hourly scheduled release rate. Under system normal conditions, fluctuations for regulation are typically short lived and generally balance out over the hour with minimal or no noticeable impacts on downstream river flow conditions. | ||
| − | Releases from Glen Canyon Dam can also fluctuate beyond scheduled releases when called upon to respond to unscheduled power outages or power system emergencies. Depending on the severity of the system emergency, the response from Glen Canyon Dam can be significant, within the full range of the operating capacity of the power plant for as long as is necessary to maintain balance in the transmission system. Glen Canyon Dam typically maintains 30 mw (approximately 880 cfs) of generation capacity in reserve in order to respond to a system emergency even when generation rates are already high. System emergencies occur fairly infrequently and typically require small responses from Glen Canyon Dam. However, these responses can have a noticeable impact on the river downstream of Glen Canyon Dam. | + | Releases from Glen Canyon Dam can also fluctuate beyond scheduled releases when called upon to respond to unscheduled power outages or power system emergencies. Depending on the severity of the system emergency, the response from Glen Canyon Dam can be significant, within the full range of the operating capacity of the power plant for as long as is necessary to maintain balance in the transmission system. Glen Canyon Dam typically maintains 30 mw (approximately 880 cfs) of generation capacity in reserve in order to respond to a system emergency even when generation rates are already high. System emergencies occur fairly infrequently and typically require small responses from Glen Canyon Dam. However, these responses can have a noticeable impact on the river downstream of Glen Canyon Dam. [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/water/crsp/cs/gcd.html] |
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 17:08, 15 February 2017
|
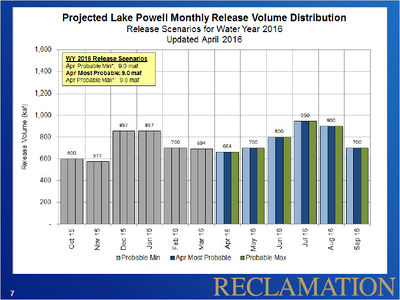
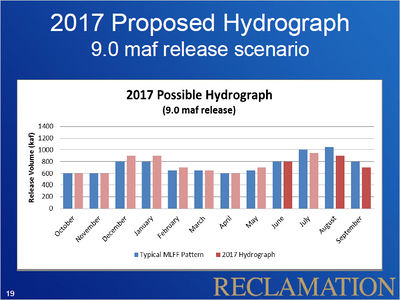
Current OperationsThe operating tier for water year 2017, established in August 2016, is the Upper Elevation Balancing Tier, with an initial water year release volume of 8.23 maf and the potential for an April 2017 adjustment to equalization or balancing releases. Based on the current forecast, an April adjustment to balancing releases is projected to occur and Lake Powell is currently projected to release 9.0 maf in water year 2017. This projection will be updated each month throughout the water year. |
| --- | --- | --- |
|---|
|
|