Difference between revisions of "Natal Origins Project (NO)"
From Glen Canyon Dam AMP
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
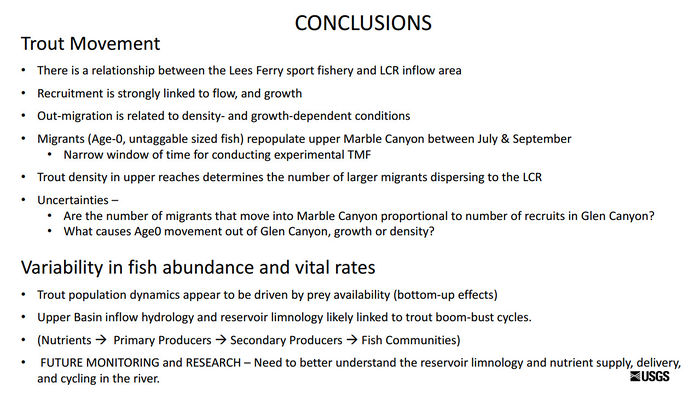
| − | + | Initial investigations found: | |
*Efficacy of Mechanical Removal | *Efficacy of Mechanical Removal | ||
*RBT abundance was high and variable, partially offset by trout immigration | *RBT abundance was high and variable, partially offset by trout immigration | ||
Revision as of 17:12, 26 April 2017
|
|
|
| -- |
-- |
-- |
|---|
|
|