Difference between revisions of "GCDAMP Sediment"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
*[https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/pp1825 East, A.E., Collins, B.D., Sankey, J.B., Corbett, S.C., Fairley, H.C., and Caster, J., 2016, Conditions and processes affecting sand resources at archeological sites in the Colorado River corridor below Glen Canyon Dam, Arizona: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1825, 104 p., http://dx.doi.org/10.3133/pp1825.] | *[https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/pp1825 East, A.E., Collins, B.D., Sankey, J.B., Corbett, S.C., Fairley, H.C., and Caster, J., 2016, Conditions and processes affecting sand resources at archeological sites in the Colorado River corridor below Glen Canyon Dam, Arizona: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1825, 104 p., http://dx.doi.org/10.3133/pp1825.] | ||
*[https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/pp1823 Topping, D.J., and Wright, S.A., 2016, Long-term continuous acoustical suspended-sediment measurements in rivers—Theory, application, bias, and error: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1823, 98 p., http://dx.doi.org/10.3133/pp1823.] | *[https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/pp1823 Topping, D.J., and Wright, S.A., 2016, Long-term continuous acoustical suspended-sediment measurements in rivers—Theory, application, bias, and error: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1823, 98 p., http://dx.doi.org/10.3133/pp1823.] | ||
| + | *[[Media:Collins 2016 GCArchSitesAeolian.pdf Brian D. Collins, David R. Bedford, Skye C. Corbett, Collin Cronkite-Ratcliff and Helen C. Fairley, 2016, Relations between rainfall–runoff-induced erosion and aeolian deposition at archaeological sites in a semi-arid dam-controlled river corridor, 19 p., Earth Surf. Process. Landforms]] | ||
*[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/16jan26/documents/AR01_Topping.pdf Project 2: Streamflow, Water Quality, Sediment Transport, and Sand Budgets in the Colorado River Ecosystem] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/16jan26/documents/AR01_Topping.pdf Project 2: Streamflow, Water Quality, Sediment Transport, and Sand Budgets in the Colorado River Ecosystem] | ||
*[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/16jan26/documents/AR02_Grams.pdf Sandbars and Sediment Storage in Marble and Grand Canyons: Response to Recent high-flow Experiments and Long-Term Trends] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/16jan26/documents/AR02_Grams.pdf Sandbars and Sediment Storage in Marble and Grand Canyons: Response to Recent high-flow Experiments and Long-Term Trends] | ||
Revision as of 12:46, 16 August 2016
|
|
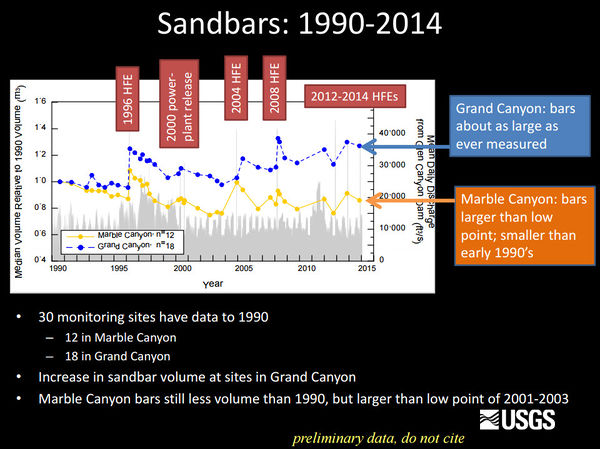
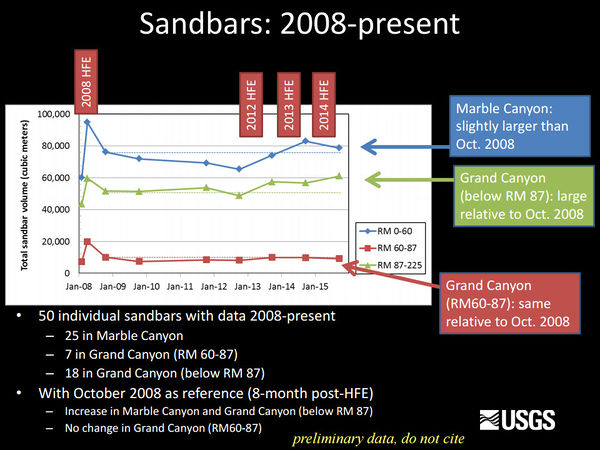
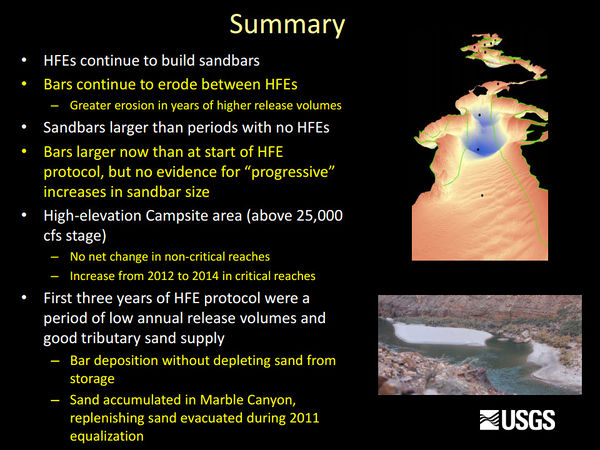
Sediment and GeomorphologyErosion of sandbars (beaches) along the Colorado River in Grand Canyon was first reported in the early 1970s, approximately 10 years after completion of Glen Canyon Dam. Since then, scientific studies have been conducted to monitor changes in sandbars and changes in the amount of sand stored on the bed of the river. One of the outcomes of these studies has been the implementation of flow experiments intended to rebuild eroded sandbars, especially by the release of controlled floods, also called “High Flow Experiments, or HFEs,” from Glen Canyon Dam. The sediment and geomorphology projects at Grand Canyon Monitoring and Research Center include the collection and processing of data to provide information needed to conduct controlled floods and to evaluate the outcome of each controlled flood and the long-term effects of controlled floods and normal dam operations on sediment-related resources.
Desired Future Condition for Sediment-Related ResourcesHigh elevation open riparian sediment deposits along the Colorado River in sufficient volume, area, and distribution so as to provide habitat to sustain native biota and desired ecosystem processes |
| --- |
--- |
--- |
|---|