Difference between revisions of "'''Oviposition and Egg Desiccation'''"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| − | [[File:EPThydropeakingModel.jpg| | + | [[File:EPThydropeakingModel.jpg|thumb|center|400px| [http://gcdamp.com/images_gcdamp_com/7/70/Kennedy_2016_HydropowerEPT.pdf BioScience Paper] ]] |
| − | [[File:MidgeAbundanceFlow.jpg|400px]] | + | [[File:MidgeAbundanceFlow.jpg|thumb|center|400px| [http://gcdamp.com/images_gcdamp_com/7/70/Kennedy_2016_HydropowerEPT.pdf BioScience Paper] ]] |
| − | [[File:DesiccationMortality.jpg|400px]] | + | [[File:DesiccationMortality.jpg|thumb|center|400px| [http://gcdamp.com/images_gcdamp_com/7/70/Kennedy_2016_HydropowerEPT.pdf BioScience Paper] ]] |
| − | [[File:EPTdiversityHydropeaking.jpg|600px]] | + | [[File:EPTdiversityHydropeaking.jpg|thumb|center|400px| [http://gcdamp.com/images_gcdamp_com/7/70/Kennedy_2016_HydropowerEPT.pdf BioScience Paper] ]] |
| + | [[File:MidgeEggStranding.jpg|thumb|center|600px|https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR19_Kennedy.pdf]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 15:06, 15 March 2018
|
|
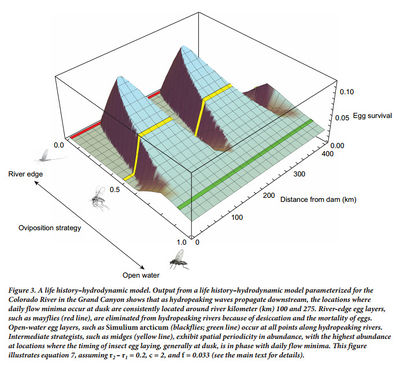
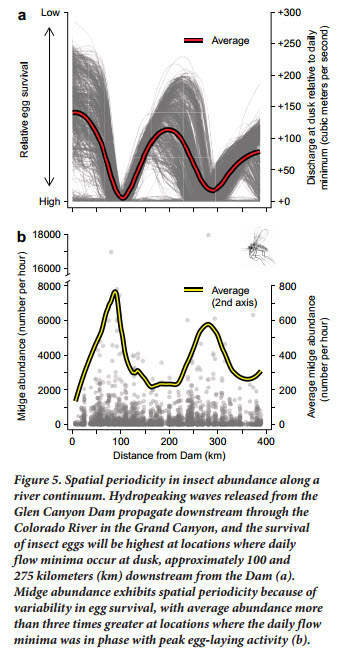
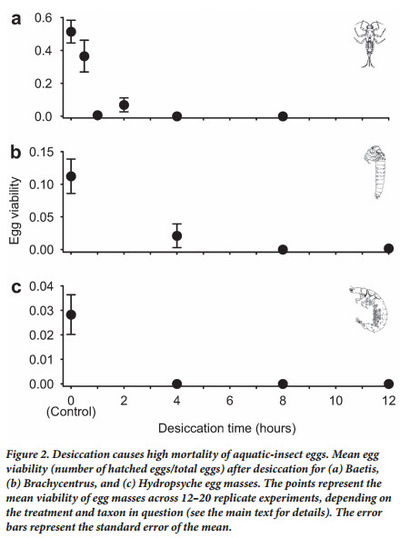
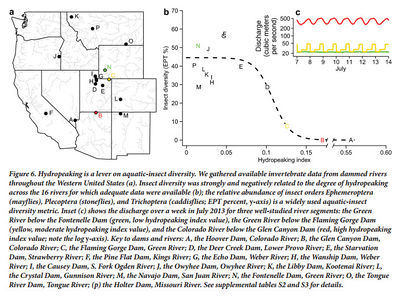
Oviposition and Egg Desiccation Studies below Flaming Gorge and Glen Canyon DamsKennedy's 2016 Bioscience paper presents a conceptual model describing how hydropower flows could be limiting aquatic insect diversity and production by limiting the reproductive success of insects accustom to laying their eggs along the shoreline. It provides supporting data from an egg desiccation study done below Flaming Gorge Dam, light trap data collected in the Grand Canyon, and a comparison of fluctuation intensity and EPT diversity in several western US hydropower tailwaters. The paper concludes that egg desiccation from fluctuating flows is likely a leading factor in limiting aquatic insect diversity and production in tailwaters below hydropower facilities. The paper also proposes a bugflow experiment to be tested at Glen Canyon Dam as a possible mitigation for fluctuating flows made for hydropower production. |
| -- |
-- |
-- |
|---|
|
|