Difference between revisions of "FOOD BASE"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
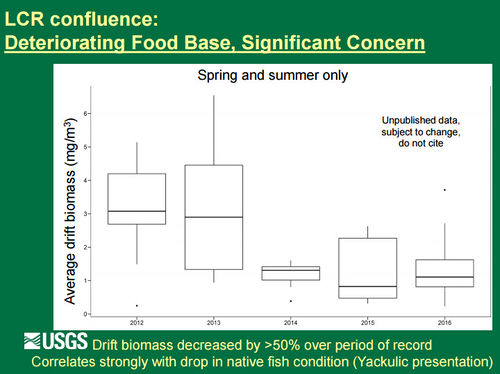
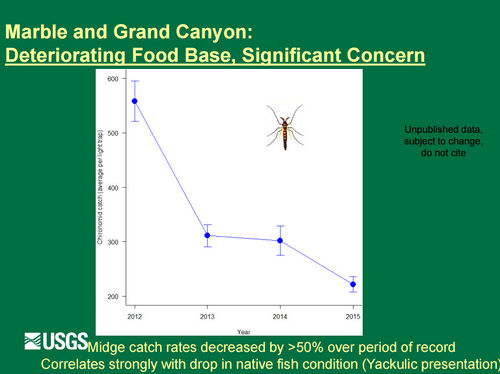
[[File:2017AR FoodbaseConclusions.jpg|thumb|center|500px| https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR19_Kennedy.pdf ]] | [[File:2017AR FoodbaseConclusions.jpg|thumb|center|500px| https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR19_Kennedy.pdf ]] | ||
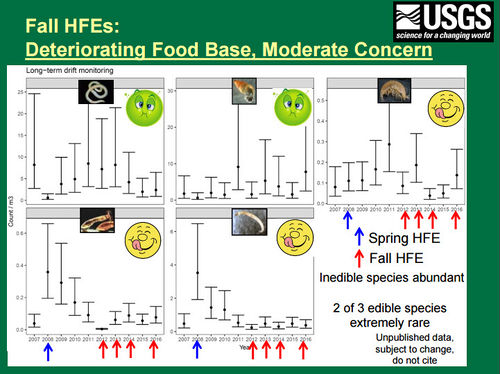
[[File:2017AR HFEsFoodbase2.jpg|thumb|center|500px| https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR19_Kennedy.pdf ]] | [[File:2017AR HFEsFoodbase2.jpg|thumb|center|500px| https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR19_Kennedy.pdf ]] | ||
| − | + | [[File:Cross 2016.JPG|thumb|center|500px|[https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2013/3039/fs2013-3039.pdf Native and Nonnative Fish Populations of the Colorado River are Food Limited—Evidence from New Food Web Analyses] ]] | |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
'''2013''' | '''2013''' | ||
| + | *[https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2013/3039/fs2013-3039.pdf Native and Nonnative Fish Populations of the Colorado River are Food Limited—Evidence from New Food Web Analyses] | ||
| + | *[http://www.montana.edu/wcross/documents/publication/Cross%20et%20al.%202013.pdf Cross et al. 2013. Food-web dynamics in a large river discontinuum. Ecological Monographs] | ||
*[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Kennedy%20et%20al.%20FWB%20proofs.pdf Kennedy et al. 2013. The relation between invertebrate drift and two primary controls, discharge and benthic densities, in a large regulated river. Freshwater Biology.] | *[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/foodbase/Kennedy%20et%20al.%20FWB%20proofs.pdf Kennedy et al. 2013. The relation between invertebrate drift and two primary controls, discharge and benthic densities, in a large regulated river. Freshwater Biology.] | ||
| − | *[http://www.uwyo.edu/bhall/reprints/wellard_kelly2013.pdf Wellard-Kelly et al. 2013. Macroinvertebrate diets reflect tributary inputs and turbidity-driven changes in food availability in the Colorado River downstream of Glen Canyon Dam. Freshwater Science | + | *[http://www.uwyo.edu/bhall/reprints/wellard_kelly2013.pdf Wellard-Kelly et al. 2013. Macroinvertebrate diets reflect tributary inputs and turbidity-driven changes in food availability in the Colorado River downstream of Glen Canyon Dam. Freshwater Science.] |
| − | *[[Media:Miller and Judson-2013-DriftAndHydropeaking.pdf| Miller and Judson. 2013. Responses of macroinvertebrate drift, benthic assemblages, and trout foraging to hydropeaking. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. | + | *[[Media:Miller and Judson-2013-DriftAndHydropeaking.pdf| Miller and Judson. 2013. Responses of macroinvertebrate drift, benthic assemblages, and trout foraging to hydropeaking. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci.]] |
*[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/13nov06/Attach_02a.pdf GCMRC Update - Status of Resources and Sediment Conditions] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/13nov06/Attach_02a.pdf GCMRC Update - Status of Resources and Sediment Conditions] | ||
*[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/annaul_reporting/Tuesday%201_22_13/6.%20Kennedy_2013Annual%20Report.pdf Annual Reporting Meeting: Foodbase Update] | *[http://www.gcmrc.gov/about/annaul_reporting/Tuesday%201_22_13/6.%20Kennedy_2013Annual%20Report.pdf Annual Reporting Meeting: Foodbase Update] | ||
Revision as of 12:25, 23 October 2019
|
|
Aquatic Food Base monitoring below Glen Canyon Dam and into Grand CanyonAquatic insects live in the water as larvae most of their lives, then emerge onto land for a brief period as winged adults. Sampling these emerged adults on land is therefore a useful tool for understanding the condition of the aquatic insect population that is in the water, particularly in large rivers where sampling the larvae on the river bed is impractical. Our group uses a variety of methods for collecting these emergent insects, which we sample principally in the Colorado River in Glen, Marble, and Grand Canyons and also in the Little Colorado River. Aquatic insects have a terrestrial, winged adult life stage in which they leave the water and fly onto land in order to find a mate and reproduce. Sampling insects at this terrestrial, adult life stage, rather than the more traditional larval, aquatic life stage, allows us to understand aquatic insect population patterns in ecosystems, such as large rivers, where sampling the aquatic larvae directly is unsafe or impractical. Our group samples these emergent adult insects primarily using sticky traps, a method we developed in-house. In the Little Colorado River, we are using these samples to understand the patterns of aquatic insect abundance throughout a river segment that is critically important to an endangered fish, the humpback chub (Gila cypha). Additionally, we collect samples monthly from Lees Ferry on the Colorado River downstream of Glen Canyon Dam to better understand patterns of food availability for recreationally-important rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). We also deploy traps throughout the Colorado River in Grand Canyon to better understand patterns of insect movement in and out of tributaries, and to describe how insect abundance varies throughout this > 250 mile stretch of river and in response to operations from Glen Canyon Dam. Sticky trap-based results from the Little Colorado River have underscored how aquatic insect abundance may be driving spatial patterns of humpback chub density and growth that are observed by cooperators at the US Fish and Wildlife Service, Arizona Game and Fish Department, and USGS. In Lees Ferry, seasonal patterns of emergent adult aquatic insects also correlate well with observed patterns of rainbow trout growth, with peaks in spring, and very low densities in winter. Thus, monitoring of insect abundance is a useful, early indicator of ecosystem health that can foretell future changes in fish population health and abundance. [1] Desired Future Condition for the Aquatic Food BaseThe aquatic food base will sustainably support viable populations of desired species at all trophic levels. Assure that an adequate, diverse, productive aquatic foodbase exists for fish and other aquatic and terrestrial species that depend on those food resources. |
| EPT as Biologic Indicators of Stream Condition |
Algae and Aquatic Macrophytes |
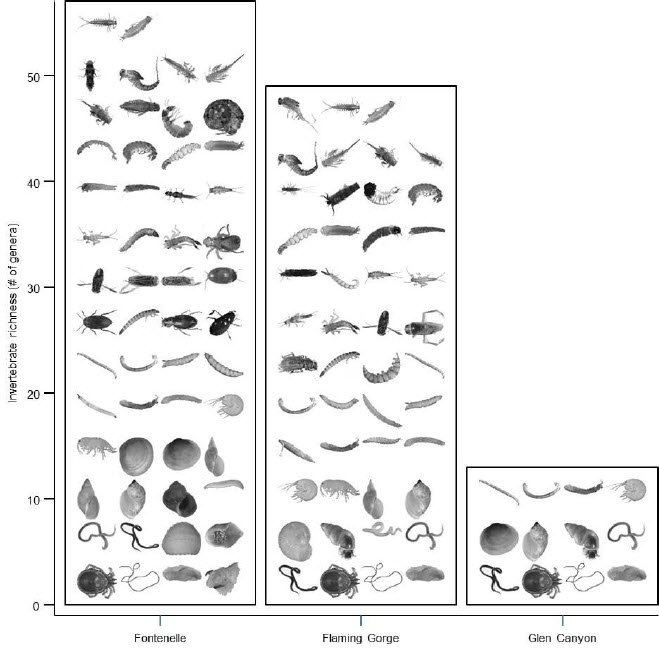
Aquatic Macroinvertebrates |
|---|