Difference between revisions of "WATER QUALITY"
From Glen Canyon Dam AMP
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
'''2024''' | '''2024''' | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2024-01-25-twg-meeting/20240125-TWGMeeting-WaterQualityConditionsLakePowell-508-UCRO.pdf Water Quality Conditions in Lake Powell and below Glen Canyon Dam ] | ||
*[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2024-01-25-twg-meeting/20240125-AnnualReportingMeeting-DissolvedOxygenDynamicsLakePowellGlenCanyon-508-UCRO.pdf Dissolved Oxygen Dynamics in Lake Powell and Glen Canyon ] | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2024-01-25-twg-meeting/20240125-AnnualReportingMeeting-DissolvedOxygenDynamicsLakePowellGlenCanyon-508-UCRO.pdf Dissolved Oxygen Dynamics in Lake Powell and Glen Canyon ] | ||
*[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2024-01-25-twg-meeting/20240125-AnnualReportingMeeting-ImprovingLakePowellCE-QUAL-W2WaterQualityModel-508-UCRO.pdf Improving the Lake Powell CE-QUAL-W2 Water Quality Model ] | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2024-01-25-twg-meeting/20240125-AnnualReportingMeeting-ImprovingLakePowellCE-QUAL-W2WaterQualityModel-508-UCRO.pdf Improving the Lake Powell CE-QUAL-W2 Water Quality Model ] | ||
Revision as of 15:33, 22 August 2024
|
|
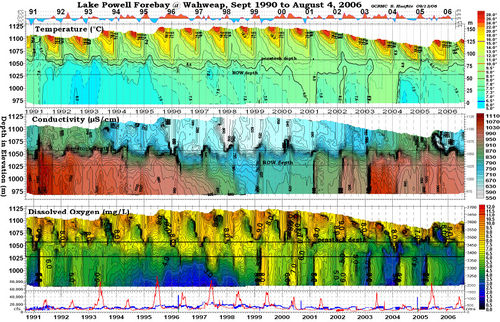
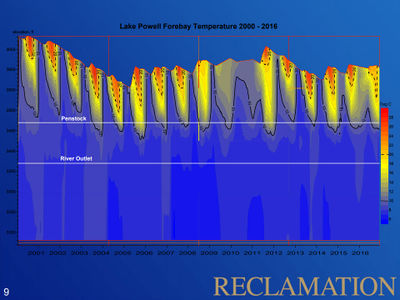
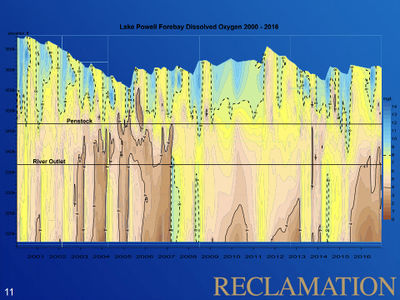
Desired Future Condition for Water QualityWater quality with regards to dissolved oxygen, nutrient concentrations and cycling, turbidity, temperature, etc., is sufficient to support natural ecosystem functions, visitor safety and visitor experience to the extent feasible and consistent with the life history requirements of focal aquatic species. |
| --- |
--- |
--- |
|---|