Difference between revisions of "HYDROPOWER"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
*[[Media:Generation at Outlet Glen Canyon Dam Plan of Study CRSP Power Peaking Capacity (March 1981).pdf|Generation at Outlet Glen Canyon Dam Plan of Study CRSP Power Peaking Capacity (March 1981)]] | *[[Media:Generation at Outlet Glen Canyon Dam Plan of Study CRSP Power Peaking Capacity (March 1981).pdf|Generation at Outlet Glen Canyon Dam Plan of Study CRSP Power Peaking Capacity (March 1981)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Ramp rates and beach stability </h2> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://asu.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/erosion-of-river-sandbars-by-diurnal-stage-fluctuations-in-the-co Alvarez and Schmeeckle (2013)] that found that the erosion of sandbars (the primary reason we have ramp rate restrictions at Glen) are not affected by ramp rates themselves. They found that erosion of sandbars is primarily caused by the higher velocity flows that washes the toe of the sandbar away which then causes the rest of the sandbar to slough off and fall into the river (i.e. mass failure). Having flows come up or go down more quickly than they do now will not increase this rate of erosion aside from the fact that the faster you can come up and go down allows you more time on peak at those higher velocity flows, which was identified as the causal factor of sandbar erosion. | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 17:51, 17 July 2019
|
|
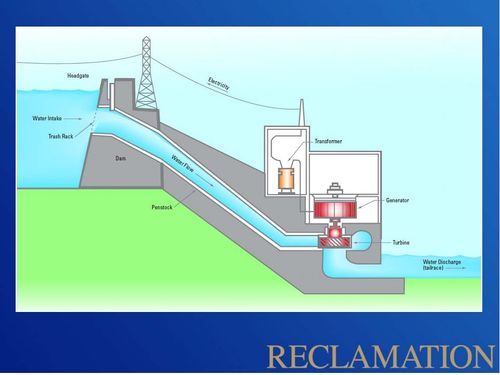
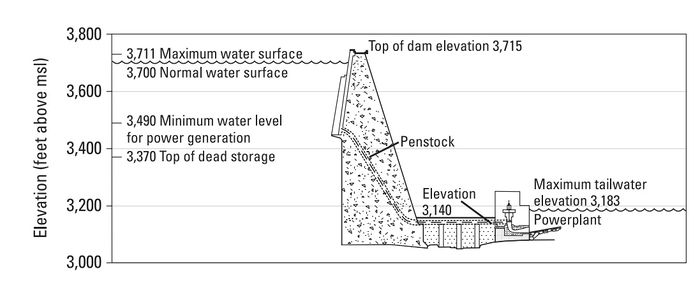
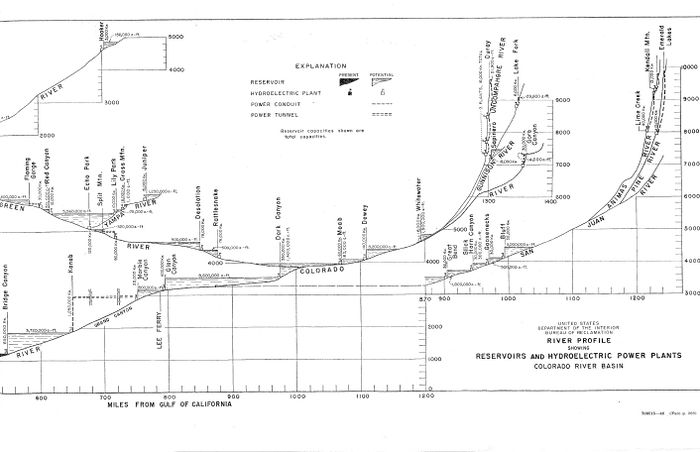
The Hydropower ResourceGlen Canyon Dam is the second highest (710 feet) concrete-arch dam in the United States, second only to Hoover Dam which stands at 726 feet. The 26.2 million acre-feet of water storage capacity in Lake Powell, created by Glen Canyon Dam, serves as a ‘bank account’ of water that is drawn on in times of drought. This stored water has made it possible to successfully weather extended dry periods by sustaining the needs of cities, industries, and agriculture throughout the West. Hydroelectric power produced by the dam’s eight generators helps meet the electrical needs of the West’s rapidly growing population. With a total capacity of 1,320 megawatts, Glen Canyon Powerplant produces around five billion kilowatt-hours of hydroelectric power annually which is distributed by the Western Area Power Administration to Wyoming, Utah, Colorado, New Mexico, Arizona, Nevada, and Nebraska. In addition, revenues from production of hydropower help fund many important environmental programs associated with Glen and Grand canyons. The designation of Glen Canyon National Recreation Area in 1972, underscores the value and importance of the recreation benefits associated with Lake Powell and the Colorado River downstream of the dam. The GCNRA is managed by the National Park Service. Glen Canyon Dam is the key water storage unit of the Colorado River Storage Project, one of the most complex and extensive river resource developments in the world. Without it, development of the Upper Colorado River Basin states’ portion of the Colorado River would not have been possible. [1] LTEMP Resource Goal for the Hydropower ResourceMaintain or increase Glen Canyon Dam electric energy generation, load following capability, and ramp rate capability, and minimize emissions and costs to the greatest extent practicable, consistent with improvement and long-term sustainability of downstream resources. Desired Future Condition for the Hydropower Resource• Glen Canyon Dam capacity and energy generation is maintained and increased, so as to produce the greatest practicable amount of power and energy, consistent with the other DFCs. |
| --- |
Hydropower - Online Training |
--- |
|---|