Difference between revisions of "CULTURAL"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
|style="width:60%; font-size:120%;"| | |style="width:60%; font-size:120%;"| | ||
| − | =='''Cultural Resources'''== | + | =='''Cultural and Archaeological Resources'''== |
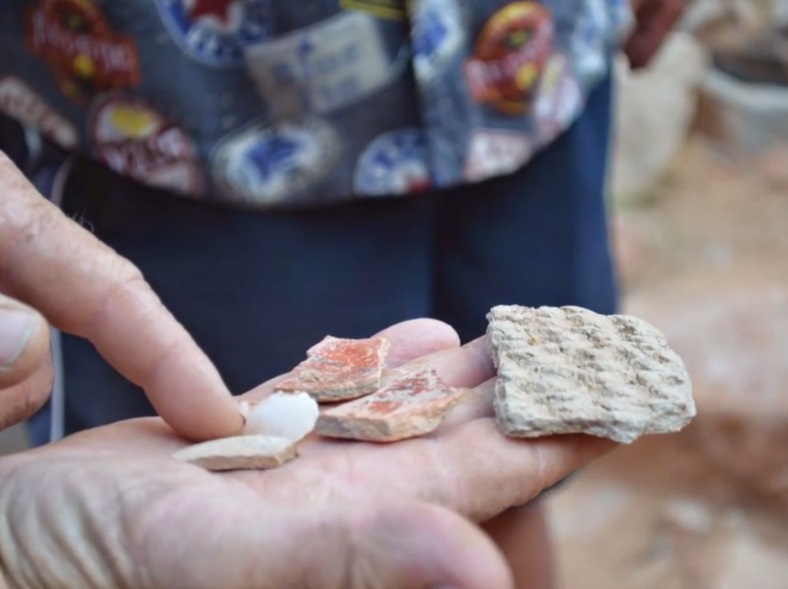
The lower reaches of Glen Canyon and the river corridor through Grand Canyon National Park, Arizona, have been used by humans for at least 13,000 years. Today, at least nine contemporary Native American Tribes claim traditional cultural ties to this area. Grand Canyon National Park contains more than 4,000 documented prehistoric and historic sites, and about 420 of these sites are located in proximity to the Colorado River. The lower reaches of Glen Canyon contain an additional 55 sites. | The lower reaches of Glen Canyon and the river corridor through Grand Canyon National Park, Arizona, have been used by humans for at least 13,000 years. Today, at least nine contemporary Native American Tribes claim traditional cultural ties to this area. Grand Canyon National Park contains more than 4,000 documented prehistoric and historic sites, and about 420 of these sites are located in proximity to the Colorado River. The lower reaches of Glen Canyon contain an additional 55 sites. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Updates</h2> | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Updates</h2> | ||
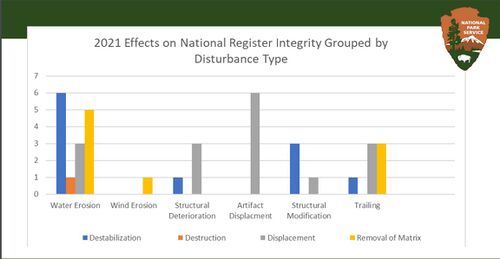
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:2021 DisturbanceType.JPG|center|500px]] [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2022-01-13-twg-meeting/20220113-AnnualReportingMeeting-2021LTEMPArchaeologicalSiteSection106Monitoring-508-UCRO.pdf https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2022-01-13-twg-meeting/20220113-AnnualReportingMeeting-2021LTEMPArchaeologicalSiteSection106Monitoring-508-UCRO.pdf] <br> |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:2021 Summary.JPG|center|500px]] [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2022-01-13-twg-meeting/20220113-AnnualReportingMeeting-2021LTEMPArchaeologicalSiteSection106Monitoring-508-UCRO.pdf https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2022-01-13-twg-meeting/20220113-AnnualReportingMeeting-2021LTEMPArchaeologicalSiteSection106Monitoring-508-UCRO.pdf] <br> |
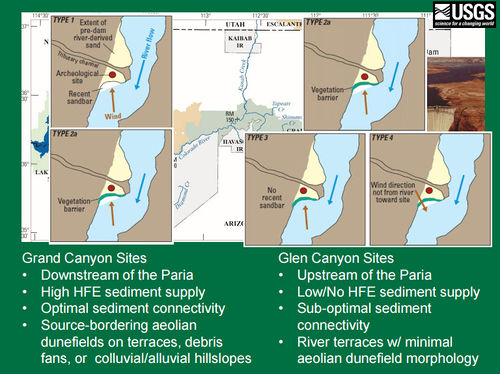
| − | [[File:AeolianOptions.jpg|center|500px]] [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR5_Sankey.pdf] | + | [[File:AeolianOptions.jpg|center|500px]] [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR5_Sankey.pdf https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR5_Sankey.pdf] <br> |
| − | [[File:AeolianTypes.jpg|center|500px]] [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR5_Sankey.pdf] | + | [[File:AeolianTypes.jpg|center|500px]] [https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR5_Sankey.pdf https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/17jan26/AR5_Sankey.pdf] <br> |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| − | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title= | + | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=Portal:GCDAMP_Knowlege_Assessments GCMRC Annual Reports page] |
| − | *[ | + | *[https://www.nps.gov/grca/learn/management/upload/CRMPIF_s.pdf 2006 Colorado River Management Plan] |
| + | *[https://www.nps.gov/grca/learn/historyculture/preservation.htm Grand Canyon National Park Archeological Resources page] | ||
| + | *[https://www.nps.gov/features/grca/001/archeology/index.html Grand Canyon River Archeology Virtual Tour] | ||
*[http://www.gcmrc.gov/research_areas/cultural_resources/cultural_resources_default.aspx USGS-GCMRC Cultural Resources Link] | *[http://www.gcmrc.gov/research_areas/cultural_resources/cultural_resources_default.aspx USGS-GCMRC Cultural Resources Link] | ||
| + | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=GCDAMP_CRAHG_Page Cultural Resources (CRAHG) AdHoc Group] | ||
| + | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=Tribal_Resources Tribal Resources Page] | ||
*[[Media:2017 LTEMP Final PA.pdf| 2017 LTEMP Programmatic Agreement]] | *[[Media:2017 LTEMP Final PA.pdf| 2017 LTEMP Programmatic Agreement]] | ||
| − | *Historic | + | *[[Media:2018 LTEMP HPP.pdf| 2018 LTEMP Historic Preservation Plan ]] |
*[[Media:Draft GCMRC Monitoring Plan w Appendix.docx| Draft plan for monitoring effects of geomorphic processes at archaeological sites in Grand & Glen Canyon. 10/7/15]] | *[[Media:Draft GCMRC Monitoring Plan w Appendix.docx| Draft plan for monitoring effects of geomorphic processes at archaeological sites in Grand & Glen Canyon. 10/7/15]] | ||
| + | *[http://gcdamp.com/index.php?title=GCDAMP-_Over-Flights Over Flights Page] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 89: | Line 94: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Questions </h2> | + | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Stakeholder Questions </h2> |
|- | |- | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Does aeolian sand transport research support the use of anthropogenic sand bar building as a means to provide a source of aeolian sands to preserve and protect archaeological sites or would current stabilization measures carried out by the NPS be more likely to be successful, predictable, and immediate at protecting archaeological sites? | ||
[[Media:Collins 2016 GCArchSitesAeolian.pdf| '''Collin et al. 2016:''' ]] | [[Media:Collins 2016 GCArchSitesAeolian.pdf| '''Collin et al. 2016:''' ]] | ||
*Aeolian deposition was found at 4 of 13 sites (30%) where partial infilling occurred preventing further erosion. | *Aeolian deposition was found at 4 of 13 sites (30%) where partial infilling occurred preventing further erosion. | ||
*“Despite this promise for archaeological site preservation, our observations show that gully annealing can only occur under a specific set of conditions related to fluvial sand availability and wind transport direction.” | *“Despite this promise for archaeological site preservation, our observations show that gully annealing can only occur under a specific set of conditions related to fluvial sand availability and wind transport direction.” | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 104: | Line 108: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="color:#000;"| | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''2024''' | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/amwg/2024-02-29-amwg-meeting/20240229-EffectsDamOperationsArchaeologicalSites-508-UCRO.pdf Effects of dam operations and vegetation management on the preservation and geomorphic condition of archaeological sites ] | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2024-01-25-twg-meeting/20240125-AnnualReportingMeeting-EffectsDamOperationsVegetationManagementPreservationGeomorphicConditionArchaeologicalSites-508-UCRO.pdf Effects of dam operations and vegetation management on the preservation and geomorphic condition of archaeological sites] | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2024-01-25-twg-meeting/20240125-AnnualReportingMeeting-MonitoringPotentialThreatsGrandCanyonRockArt-508-UCRO.pdf Monitoring for Potential Threats to Grand Canyon Rock Art ] | ||
| + | *[[Media:Tango ARM2024 Poster IPDS.pdf| River management influences on archaeological site preservation: Results of more than a decade of monitoring geomorphic change along the Colorado River]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''2023'''' | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2023-04-13-twg-meeting/20230413-Section106NationalHistoricPreservationAct-508-UCRO.pdf Section 106 of the National Historic Preservation Act] | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2023-01-26-twg-meeting/20230126-AnnualReportingMeeting-ArchaeologicalSitesErodingGrandCanyonOwingSixDecadesGle%20CanyonDamOperations-508-UCRO.pdf Archaeological Sites are Eroding in Grand Canyon Owing to Six Decades of Glen Canyon Dam Operations: Floods, Low Flows and Vegetation Management Can Help] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''2022''' | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/amwg/2022-08-18-amwg-meeting/20220818-Nelson-LTEMP-PA2022Summary_508.pdf Glen Canyon’s LTEMP Annual Cultural PA Meeting 2022] | ||
| + | *[https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2022/1097/ofr20221097.pdf Caster et al., 2022, Terrestrial lidar monitoring of the effects of Glen Canyon Dam operations on the geomorphic condition of archaeological sites in Grand Canyon National Park, 2010–2020] | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/amwg/2022-02-10-amwg-meeting/20220210-NPS-USGSArchaeologicalSiteMonitoringResearch-508-UCRO.pdf NPS and USGS Archaeological Site Monitoring and Research ] | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2022-01-13-twg-meeting/20220113-AnnualReportingMeeting-2021LTEMPArchaeologicalSiteSection106Monitoring-508-UCRO.pdf 2021 LTEMP Archaeological Site Section 106 Monitoring ] | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2022-01-13-twg-meeting/20220113-AnnualReportingMeeting-CulturalBenefitsActionOpportunityFramework-508-UCRO.pdf Cultural Benefits Action Opportunity Framework ] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''2020''' | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/amwg/2020-02-12-amwg-meeting/20200212-GCMRCScienceUpdatesPart3-Presentation-508-UCRO.pdf GCMRC 2019 Annual Reporting Meeting Overview – Part 3 ] | ||
'''2018''' | '''2018''' | ||
| Line 150: | Line 174: | ||
*[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2009-03-16-twg-meeting/Attach_12f.pdf Geoarchaeological investigations and an archaelogical treatment plan for 151 sites in Grand Canyon, Arizona] | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2009-03-16-twg-meeting/Attach_12f.pdf Geoarchaeological investigations and an archaelogical treatment plan for 151 sites in Grand Canyon, Arizona] | ||
*[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2009-03-16-twg-meeting/Attach_13.pdf Analysis of Virtual Shorelines in Relation to Archaeological Sites in the Colorado river Ecosystem PPT] | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/progact/amp/twg/2009-03-16-twg-meeting/Attach_13.pdf Analysis of Virtual Shorelines in Relation to Archaeological Sites in the Colorado river Ecosystem PPT] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
Latest revision as of 11:32, 23 August 2024
|
|
Cultural and Archaeological ResourcesThe lower reaches of Glen Canyon and the river corridor through Grand Canyon National Park, Arizona, have been used by humans for at least 13,000 years. Today, at least nine contemporary Native American Tribes claim traditional cultural ties to this area. Grand Canyon National Park contains more than 4,000 documented prehistoric and historic sites, and about 420 of these sites are located in proximity to the Colorado River. The lower reaches of Glen Canyon contain an additional 55 sites. In addition to archaeological sites, cultural resources along the Colorado River corridor include historic structures and other types of historic properties, as well as biological and physical resources that are of traditional cultural importance to Native American peoples such as springs, unique landforms, mineral deposits, native plant concentrations, and various animal species. LTEMP Resource Goal for Archaeological and Cultural ResourcesMaintain the integrity of potentially affected NRHP-eligible or listed historic properties in place, where possible, with preservation methods employed on a site-specific basis. Desired Future Condition for Cultural ResourcesPrehistoric Archaeological Sites and Historic Sites: |
| Tribal Ecological Knowledge |
Cultural Resources Library |
Tribal Perspectives |
|---|