Difference between revisions of "Tribal Resources"
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 177: | Line 177: | ||
'''2011''' | '''2011''' | ||
*[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/11aug24/Attach_14.pdf AIF: Tribal Liaison Report and PPT] | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/11aug24/Attach_14.pdf AIF: Tribal Liaison Report and PPT] | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/11may18/Attach_09a.pdf AIF: Tribal Liaison Report and PPT] | ||
| + | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/amwg/mtgs/11may18/Attach_09b.pdf Federal Register Notice: Request for Comments on Consultation with Indian Tribes] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 16:15, 30 June 2017
|
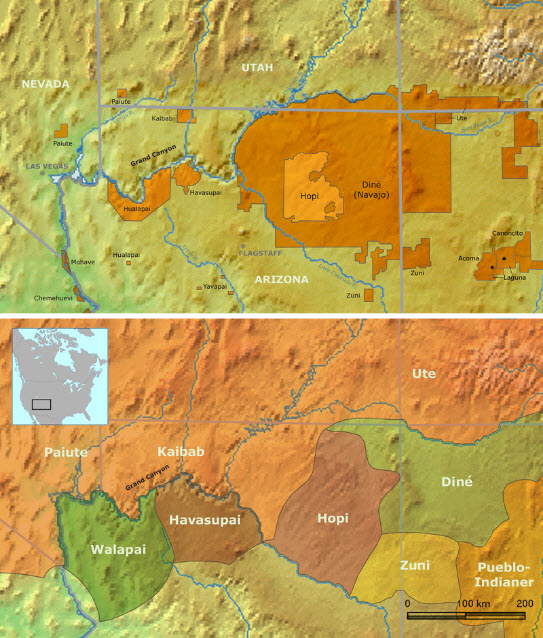
Homelands and reservations of Native Americans associated with the Grand Canyon [1] |
Tribal ResourcesThe lower reaches of Glen Canyon and the river corridor through Grand Canyon National Park, Arizona, have been used by humans for at least 13,000 years. Today, at least nine contemporary Native American Tribes claim traditional cultural ties to this area. Grand Canyon National Park contains more than 4,000 documented prehistoric and historic sites, and about 420 of these sites are located in proximity to the Colorado River. The lower reaches of Glen Canyon contain an additional 55 sites. In addition to archaeological sites, cultural resources along the Colorado River corridor include historic structures and other types of historic properties, as well as biological and physical resources that are of traditional cultural importance to Native American peoples such as springs, unique landforms, mineral deposits, native plant concentrations, and various animal species. LTEMP Resource Goal for Tribal ResourcesMaintain the diverse values and resources of traditionally associated Tribes along the Colorado River corridor through Glen, Marble, and Grand Canyons. Desired Future Condition for Cultural ResourcesTraditional Cultural Properties (TCPs):
|
| Tribal Ecological Knowledge |
Cultural Resources Library |
Tribal Perspectives |
|---|