Difference between revisions of "WATER QUALITY"
From Glen Canyon Dam AMP
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
Cellsworth (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
*[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14apr08/TWP_14jun06.pdf?bcsi_scan_cf0ea36431a6106e=xBHF7QVHXt6Zx5nJZ4cG0wktr3sHAAAA6aC3BQ==&bcsi_scan_filename=TWP_14jun06.pdf Glen Canyon Dam Adaptive Management Program Triennial Budget and Work Plan— Fiscal Years 2018–2020] | *[https://www.usbr.gov/uc/rm/amp/twg/mtgs/14apr08/TWP_14jun06.pdf?bcsi_scan_cf0ea36431a6106e=xBHF7QVHXt6Zx5nJZ4cG0wktr3sHAAAA6aC3BQ==&bcsi_scan_filename=TWP_14jun06.pdf Glen Canyon Dam Adaptive Management Program Triennial Budget and Work Plan— Fiscal Years 2018–2020] | ||
*[https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2008/1153/ USGS Workshop on Scientific Aspects of a Long-Term Experimental Plan for Glen Canyon Dam, April 10–11, 2007, Flagstaff, Arizona] | *[https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2008/1153/ USGS Workshop on Scientific Aspects of a Long-Term Experimental Plan for Glen Canyon Dam, April 10–11, 2007, Flagstaff, Arizona] | ||
| − | *[[Media:Jones 2001 Final report PEP GCMRC IWQP.pdf| Final report of the Protocol Evaluation Panel for the Grand Canyon Monitoring and Research Center Integrated Water Quality Program (IWQP)]] | + | *[[Media:Jones 2001 Final report PEP GCMRC IWQP.pdf| Final report of the 2001 Protocol Evaluation Panel for the Grand Canyon Monitoring and Research Center Integrated Water Quality Program (IWQP)]] |
*[https://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/471/pdf/ds471.pdf Historical Physical and Chemical Data for Water in Lake Powell and from Glen Canyon Dam Releases, Utah-Arizona, 1964–2013] | *[https://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/471/pdf/ds471.pdf Historical Physical and Chemical Data for Water in Lake Powell and from Glen Canyon Dam Releases, Utah-Arizona, 1964–2013] | ||
*[https://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/1282/ The State of the Colorado River Ecosystem in Grand Canyon: A report of the Grand Canyon Monitoring and Research Center 1991-2004] | *[https://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/1282/ The State of the Colorado River Ecosystem in Grand Canyon: A report of the Grand Canyon Monitoring and Research Center 1991-2004] | ||
| Line 171: | Line 171: | ||
'''2005''' | '''2005''' | ||
*[http://www.usbr.gov/newsroom/newsrelease/detail.cfm?RecordID=8041 Reclamation to continue experimental operations at Glen Canyon Dam; Efforts address low dissolved oxygen levels below dam] | *[http://www.usbr.gov/newsroom/newsrelease/detail.cfm?RecordID=8041 Reclamation to continue experimental operations at Glen Canyon Dam; Efforts address low dissolved oxygen levels below dam] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! <h2 style="margin:0; background:#cedff2; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Water Quality PEP Reviews </h2> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="color:#000;"| | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Media:Jones 2001 Final report PEP GCMRC IWQP.pdf| Final report of the 2001 Protocol Evaluation Panel for the Grand Canyon Monitoring and Research Center Integrated Water Quality Program (IWQP)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 31 October 2017
|
|
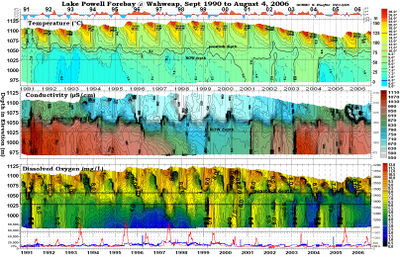
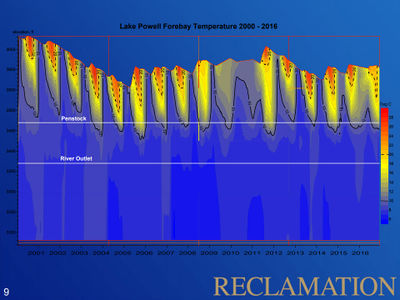
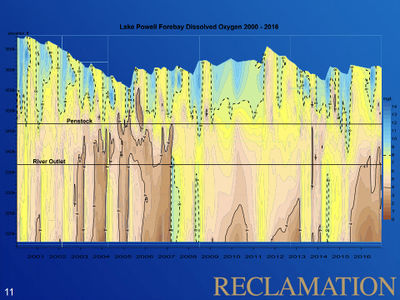
Desired Future Condition for Water QualityWater quality with regards to dissolved oxygen, nutrient concentrations and cycling, turbidity, temperature, etc., is sufficient to support natural ecosystem functions, visitor safety and visitor experience to the extent feasible and consistent with the life history requirements of focal aquatic species. |
| --- |
--- |
--- |
|---|